Model Training via SSH¶
This describes how to train a machine learning model on a remote machine via SSH. This is useful as it allows for developing a model on a local, resource-constrained machine and then seamlessly train the model on a much larger remote “cloud” server.
Quick Reference¶
Command-line: mltk ssh –help
Tutorial: Cloud Training with vast.ai
Overview¶
The MLTK features the command: mltk ssh which internally manages all of the details necessary to execute an MLTK command on a remote machine.
The basic flow for training a model in the cloud is as as follows:
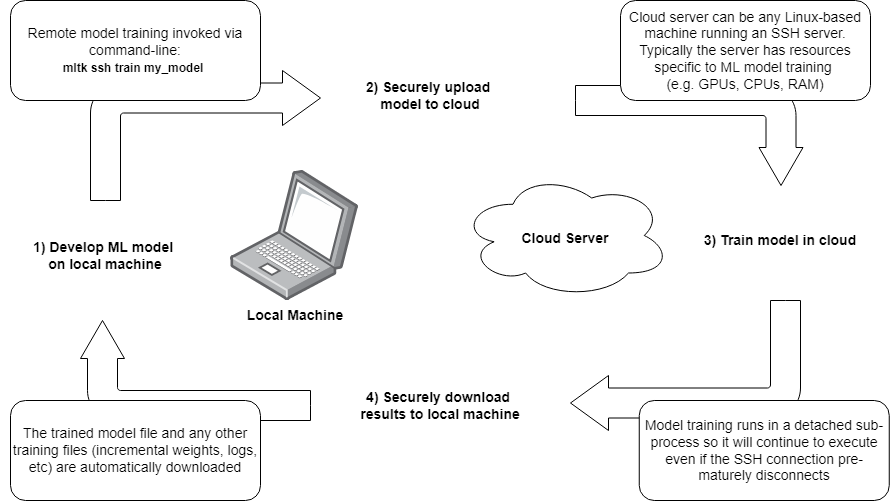
Create a model specification on a local machine
Invoke the command:
mltk ssh train my_model, which will:
a. Open a secure connection to a remote machine
b. Upload all necessary files to the remote machineInvoke the train command on the remote machine (which may have a large amount of GPUs/CPUs/RAM)
After training completes on the remote machine, the model archive and any other training files are downloaded to the local machine
So basically, develop the model on the local machine, quickly train it on a cloud machine, and all training results appear on the local machine as if the model had been trained locally.
SSH Connection¶
SSH is a standard protocol for securely connecting to remote machines. With it, shell commands may be issued from a local machine and executed on a remote machine.
While the details of creating an SSH connection is out-of-scope for this document, it is important to note the following:
The SSH Server runs on the remote machine
The SSH Client runs on the local machine
OpenSSH is a free, open-source tool that provides both the an SSH client and server which are available for Windows, Linux, and Mac.
The OS of the client does not need to match the server, e.g. a Windows SSH client can connect to a Linux SSH server
Installing an SSH client¶
While an SSH client does not need to be installed on the local machine,
it is helpful to have one to ensure the login credentials are working before using the mltk ssh command (which internally uses its own SSH client python library).
Windows¶
Refer to the following documentation for how to install the SSH client on Windows: Get started with OpenSSH
Linux¶
On Linux, the SSH client is likely installed by default. However, on Ubuntu-like systems, it can be installed with:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install openssh-client
Generating a Keypair¶
A keypair is required to securely connect to the SSH server. The details of creating and distributing the keypair are out-of-scope for this document, however, it is important to note the following:
A keypair consists of one private key and one public key
The private key resides on the local machine, its contents must be securely stored (i.e. do not share it with others)
The public key resides on the remote machine, its contents need not be secure (i.e. it can be copied & pasted anywhere)
Command¶
The MLTK features a helper command for generating an SSH keypair:
mltk ssh-keygen --help
Which will generate an Ed25519 keypair in the specified output directory., e.g.:
# Generate pair at: ~/.ssh/id_my_key
mltk ssh-keygen my_key
Additional Resources¶
Refer to the following for additional information on creating and distributing a keypair:
Command sequence¶
When the mltk ssh <command> command is invoked, the following sequence is internally executed:
Open an SSH connection to remote server
Using the settings specified in the--hostoption, in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, or in~/.ssh/configCreate remote working directory
Specified in--hostoption or in~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlCreate and activate an MLTK python virtual environment
Only if not disabled in model specification or~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlUpload files configured in model specification and/or
~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlExport any environment variables configured in model specification and/or
~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlExecute any startup shell commands configured in model specification and/or
~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlExecute the MLTK
<command>in a detached subprocess
This way, the command continues to execute even if the SSH session prematurely disconnectsPoll the remote MLTK command subprocess while dumping the remote log file to the local terminal
Issuing CTRL+C will abort the remote command subprocess (Use the--no-waitoption to skip this step)Once the MLTK command completes, download the model archive file (if available)
Download any files configured in model specification and/or
~/.mltk/user_settings.yamlDownload any other logs files
Execute any shutdown shell commands configured in model specification and/or
~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml
Settings¶
The following settings are used by the mltk ssh command.
Note that most of these settings are optional and may be configured
in several different locations (see the next section, “Settings Locations”, for more details).
Remote Working Directory¶
This is the working directory where the MLTK command will execute.
This setting is optional
Default:
.
This setting can be specified in one of three locations (in order of priority):
The
--hostcommand-line option, e.g.
mltk ssh --host my_server.com/workspaceThe
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.remote_dir = '~/workspaceThe
ssh.remote_dirsetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: remote_dir: ~/workspace
Hostname¶
The name of the SSH server. This can be:
Domain name of server, e.g.: myserver.com
IP address, e.g.: 145.243.23.222
Host name in ~/.ssh/config
This setting is required.
This setting can be specified in one of three locations (in order of priority):
The
hostnamein ~/.ssh/config that maps to theHostprovided on the command-line with the--hostoption, e.g.:
mltk ssh --host my_server-> findHostentry in~/.ssh/configwith namemy_server-> Use correspondingHostnamevalueThe
--hostcommand-line option, e.g.
mltk ssh --host myserver.comThe
ssh.connection.hostnamesetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: connection: hostname: myserver.com
Port¶
The listening port of the SSH server.
This setting is optional
Default:
22
This setting can be specified in one of four locations (in order of priority):
The
--portcommand-line option, e.g.:
mltk ssh --host ssh3.vast.ai -p 34567-> port=34567The
--hostcommand-line option, e.g.
mltk ssh --host ssh3.vast.ai:34567-> port=34567The
Userin ~/.ssh/config that maps to theHostprovided on the command-line with the--hostoption, e.g.:
mltk ssh --host my_server-> findHostentry in~/.ssh/configwith namemy_server-> Use correspondingPortvalueThe
ssh.connection.portsetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: connection: port: 2222
Username¶
The SSH login username.
This setting is optional
This setting can be specified in one of three locations (in order of priority):
The
--hostcommand-line option, e.g.
mltk ssh --host root@ssh3.vast.ai:34567-> username=rootThe
Userin ~/.ssh/config that maps to theHostprovided on the command-line with the--hostoption, e.g.:
mltk ssh --host my_server-> findHostentry in~/.ssh/configwith namemy_server-> Use correspondingUservalueThe
ssh.connection.usernamesetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: connection: username: root
Key Filename¶
The filepath to the SSH private key.
This setting is optional
This setting can be specified in one of three locations (in order of priority):
The
-icommand-line option, e.g.
mltk ssh myserver.com -i ~/.ssh/id_myserverThe
IdentityFilein ~/.ssh/config that maps to theHostprovided on the command-line with the--hostoption, e.g.:
mltk ssh --host my_server-> findHostentry in~/.ssh/configwith namemy_server-> Use correspondingIdentityFilevalueThe
ssh.connection.key_filenamesetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: connection: key_filename: ~/.ssh/id_myserver
Environment¶
List or dictionary of environment variables to export before executing MLTK command on remote server.
This setting is optional
This setting can be specified in two locations (in order, higher is merged with lower (so higher overwrites lower)):
The
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.environment = ['PROD_ENV=1', 'CUDA_DEVICES=2']or
my_model.environment = dict(PROD_ENV=1, CUDA_DEVICES=2)The
ssh.environmentsetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: environment: - PROD_ENV=1 - CUDA_DEVICES=
or
ssh: environment: PROD_ENV: 1 CUDA_DEVICES: 2
Upload Files¶
List of file paths to upload from the local to remote before executing MLTK command.
This setting is optional
If the path does not contain a pipe |, e.g.: dataset/*.csv, then:
The local path is relative to the model specification script
The remote path is relative to the remote working directory
Absolute paths are not allowed
The path may use the recursive glob format
If the path does contain a pipe |, e.g.: ~/patch.txt|./patch.txt, then:
Format is
<local path>|<remote path>The local path is relative to the model specification script
The remote path is relative to the remote working directory
Both paths may be absolute
No wildcards
This setting can be specified in two locations (in order, higher is appended lower):
The
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.upload_files = ['dataset.zip', 'dataset/*.csv']The
ssh.upload_filessetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: upload_files: - dataset.zip - dataset/*.csv - ~/patch.txt|./patch.txt
Startup Commands¶
List of shell commands to execute on remote machine before executing the MLTK command.
This setting is optional
The commands run in a bash shell
This setting can be specified in two locations (in order, higher is appended lower):
The
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.startup_cmds = ['pip install mylib', 'sudo apt-get install 7zip']The
ssh.startup_cmdssetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: startup_cmds: - pip install mylib - sudo apt-get install 7zip
Download Files¶
List of file paths to download from the remote to local after executing MLTK command.
This setting is optional
If the path does not contain a pipe |, e.g.: logs/*.txt, then:
The local path is relative to the model specification script
The remote path is retlavie to the remote working directory
Absolute paths are not allowed
The path may use the recursive glob format
If the path does contain a pipe |, e.g.: ./results.txt|~/results.txt, then:
Format is
<remote path>|<local path>The local path is relative to the model specification script
The remote path is relative to the remote working directory
Both paths may be absolute
No wildcards
This setting can be specified in two locations (in order, higher is appended lower):
The
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.download_files = ['results.zip', 'logs/*.txt']The
ssh.download_filessetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: download_files: - results.zip - logs/*.txt - ./results.txt|~/results.txt
Shutdown Commands¶
List of shell commands to execute on remote machine after executing the MLTK command.
This setting is optional
The commands run in a bash shell
This setting can be specified in two locations (in order, higher is appended lower):
The
SshMixinmodel mixin property, e.g.
my_model.shutdown_cmds = ['curl -F data=log.txt my_server.com']The
ssh.shutdown_cmdssetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: shutdown_cmds: - curl -F `data=log.txt` my_server.com
Sync Local MLTK¶
This flags allows for syncing the local MLTK into the remote MLTK. This is useful if changes have been made to the local MLTK that are not in the public MLTK python package.
This setting is optional
Default:
false
The
ssh.sync_local_mltksetting in~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.ssh: sync_local_mltk: true
Settings Locations¶
The various settings may be specified in the following locations:
Command-line options¶
There are three command-line options:
–host¶
mltk ssh --host [<user name>@]<host>[:<port>][/<path>]
Where:
<user name>- Optional, user login name<host>- Required, SSH hostname or name in ~/.ssh/config<port>- Optional, SSH port, default is 22<path>- Optional, remote directory path
Examples:
mltk ssh --host my_servermltk ssh --host myserver.commltk ssh --host 192.168.1.56mltk ssh --host ubuntu@192.168.1.56mltk ssh --host ubuntu@192.168.1.56:456mltk ssh --host ubuntu@192.168.1.56/workspace
–port¶
mltk ssh --port <port>
Where:
<port>is the SSH server’s listening port
–identity_file¶
mltk ssh --identity_file <file path>
Where:
<file path>- Is the file path to the SSH private key
SshMixin¶
The SshMixin model mixin allows for defining model-specific SSH settings.
NOTE: This mixin is optional, it is not required to run the model with the ssh command.
Example¶
# Import MLTK model object and mixins
from mltk.core import (
MltkModel,
TrainMixin,
AudioDatasetMixin,
EvaluateClassifierMixin,
SshMixin,
)
# Instantiate MltkModel with SshMixin
class MyModel(
MltkModel,
TrainMixin,
AudioDatasetMixin,
EvaluateClassifierMixin,
SshMixin
):
pass
my_model = MyModel()
# Define model-specific SSH properties
my_model.ssh_remote_dir = '~/workspace'
my_model.ssh_create_venv = True
my_model.ssh_environment = ['DEV=1', 'CUDA_DEVICES=2']
my_model.ssh_startup_cmds = ['pip install mylib']
my_model.ssh_upload_files = ['dataset.zip', 'dataset/*.csv']
my_model.ssh_download_files = ['results.zip']
my_model.ssh_shutdown_cmds = ['echo "all done"']
~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml¶
The user_settings.yaml file allows for defining user-specific MLTK settings.
This file must be manually created at ~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml.
The following SSH settings may be added to this file (all settings are optional):
ssh:
config_path: <path to ssh config file on local machine>
remote_dir: <path to remote working directory>
create_venv: <true/false, if a MLTK python venv should be automatically created on the remote machine>
connection:
hostname: <SSH server hostname>
port: <SSH server listening port>
username: <user login name>
key_filename: <path to private key on local machine>
environment: <list of environment variables to export on remote machine>
upload_files: <list of files to upload to remote machine>
startup_cmds: <list of shell commands to execute on remote machine before executing MLTK command>
download_files: <list of files to download after executing MLTK command>
shutdown_cmds: <list of shell commands to execute after executing MLTK command>
Example¶
File: ~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml:
ssh:
config_path: ~/ssh_config
remote_dir: ~/workspace
create_venv: false
connection:
hostname: my_server.com
port: 222
username: joe
key_filename: ~/.ssh/id_my_server
environment:
- CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=-1
- DEV_ENV=1
upload_files:
- dataset.zip
- config.txt
startup_cmds:
- pip install silabs-mltk
- sudo apt install -y p7zip-full libsndfile1
download_files:
- custom_logs/**
shutdown_cmds:
- curl -F `data=log.txt` my_server.com
~/.ssh/config¶
The SSH Config file is a standard file used by the SSH client.
By default, this file is located at ~/.ssh/config. This path can be overridden by defining the ssh.config_path setting
in ~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml, e.g.:
ssh:
config_path: custom/path/ssh/config
Refer to the online documentation for more details about the contents of this file: SSH Config
Example¶
File: ~/.ssh/config:
Host vast_ai
HostName ssh6.vast.ai
Port 31521
User root
StrictHostKeyChecking no
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_vast_ai
Then issuing the following command will use the config file settings:
mltk ssh --host vast_ai train image_example1
Command Examples¶
Executing MLTK commands on a remote machine via SSH is done using the ssh operation.
For more details on the available command-line options, issue the command:
mltk ssh --help
When a command is invoked, it executes in a detached sub-process. This way, if the SSH connection prematurely disconnects, the command will continue to execute.
Issuing Ctrl+C will abort the command on both the local and remote machines.
The following are examples of how remote SSH training can be invoked from the command-line:
Example 1: Train with settings configured in user_settings.yaml¶
The following shows how to train the keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 model on a remote server.
In this example, all of the SSH settings are configured in the ~/.mltk/user_settings.yaml.
After training completes, the results are downloaded to the local machine.
mltk ssh train keyword_spotting_on_off_v3
Example 2: Train with settings on command-line¶
The following shows to train the keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 model on a remote server.
In this example, the SSH server settings are provided on the command-line.
After training completes, the results are downloaded to the local machine.
mltk ssh -h root@ssh5.vast.ai/workspace -p 23452 -i ~/.ssh/id_vast_ai train keyword_spotting_on_off_v3
The -h option has the following format: [<user name>@]<host>[:<port>][/<path>]
where:
<user name>- user login name (optional)<host>- SSH server hostname<port>- SSH server listening port (optional)<path>- Remote directory path (optional)
The -p is the SSH server’s listening port.
And the -i option points to the SSH private key file on the local machine.
Example 3: Train without wait for results¶
The following shows to train the keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 model on a remote server.
In this example, the SSH server hostname is provided and the login info is retrieved from the ~/.ssh/config file.
Since the --no-wait option is provided, the command does not wait for the training to complete on the remote server.
Instead, the command immediately returns and the training command executes on the remote server in the background.
To retrieve the training results, the --resume option was be later provided (see Example 4 below).
mltk ssh -h vast.ai train keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 --no-wait
Example 4: Retrieve results from previous training session¶
The following shows how to retrieve the results of a previously executed command.
This is useful if SSH connection prematurely disconnects or the --no-wait option was previously used.
This will wait until the previously invoked command has completed on the remote server then download the training results.
mltk ssh -h vast.ai train keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 --resume
HINT: You could also use the --no-wait option to poll the remote server to see if the command has completed without waiting for it to finish.
Example 5: Train new model, and forcefully discard previous¶
Only one command may be active on the remote server. The --force option may be used to abort a previously invoked command.
mltk ssh train keyword_spotting_on_off_v3 --force