rock_paper_scissors¶
Source code: rock_paper_scissors.py.
Pre-trained model: rock_paper_scissors.mltk.zip.
This provides an example of how to define a classification model that uses the Rock/Paper/Scissors dataset with the ParallelImageGenerator as its data source.
The basic flow for the ML model is:
96x96x1 grayscale image of hand gesture -> ML Model -> [result vector]
Where [result vector] is a 3 element array with each element containing the % probability that the given image is a “rock”, “paper”, “scissor”, or _unknown_ hand gesture.
Commands¶
# Do a "dry run" test training of the model
mltk train rock_paper_scissors-test
# Train the model
mltk train rock_paper_scissors
# Evaluate the trained model .tflite model
mltk evaluate rock_paper_scissors --tflite
# Profile the model in the MVP hardware accelerator simulator
mltk profile rock_paper_scissors --accelerator MVP
# Profile the model on a physical development board
mltk profile rock_paper_scissors --accelerator MVP --device
# Dump some of the augmented images
mltk custom rock_paper_scissors dump --count 100
# Run this model in the image classifier application
mltk classify_image rock_paper_scissors --dump-images
Model Summary¶
mltk summarize rock_paper_scissors --tflite
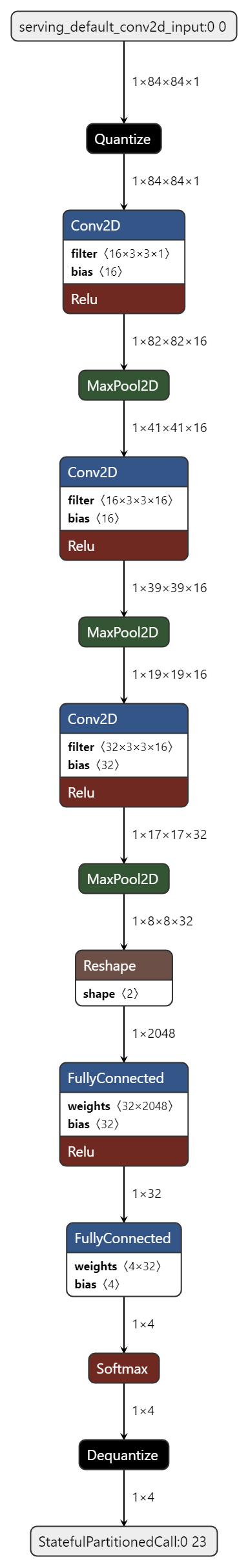
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | Input(s) | Output(s) | Config |
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | quantize | 84x84x1 (float32) | 84x84x1 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 1 | conv_2d | 84x84x1 (int8) | 82x82x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x1 (int8) | | |
| | | 16 (int32) | | |
| 2 | max_pool_2d | 82x82x16 (int8) | 41x41x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 3 | conv_2d | 41x41x16 (int8) | 39x39x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x16 (int8) | | |
| | | 16 (int32) | | |
| 4 | max_pool_2d | 39x39x16 (int8) | 19x19x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 5 | conv_2d | 19x19x16 (int8) | 17x17x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x16 (int8) | | |
| | | 32 (int32) | | |
| 6 | max_pool_2d | 17x17x32 (int8) | 8x8x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 7 | reshape | 8x8x32 (int8) | 2048 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| | | 2 (int32) | | |
| 8 | fully_connected | 2048 (int8) | 32 (int8) | Activation:relu |
| | | 2048 (int8) | | |
| | | 32 (int32) | | |
| 9 | fully_connected | 32 (int8) | 4 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 32 (int8) | | |
| | | 4 (int32) | | |
| 10 | softmax | 4 (int8) | 4 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=9 |
| 11 | dequantize | 4 (int8) | 4 (float32) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Total MACs: 5.870 M
Total OPs: 12.050 M
Name: rock_paper_scissors
Version: 1
Description: Image classifier example for detecting Rock/Paper/Scissors hand gestures in images
Classes: rock, paper, scissor, _unknown_
hash: 9b557f35e32df7614723ddaafd77d75f
date: 2022-05-02T23:18:20.997Z
runtime_memory_size: 137176
detection_threshold: 175
average_window_duration_ms: 500
minimum_count: 2
suppression_count: 1
samplewise_norm.rescale: 0.0
samplewise_norm.mean_and_std: True
.tflite file size: 80.2kB
Model Profiling Report¶
# Profile on physical EFR32xG24 using MVP accelerator
mltk profile rock_paper_scissors --device --accelerator MVP
Profiling Summary
Name: rock_paper_scissors
Accelerator: MVP
Input Shape: 1x84x84x1
Input Data Type: float32
Output Shape: 1x4
Output Data Type: float32
Flash, Model File Size (bytes): 80.2k
RAM, Runtime Memory Size (bytes): 137.3k
Operation Count: 12.3M
Multiply-Accumulate Count: 5.9M
Layer Count: 12
Unsupported Layer Count: 0
Accelerator Cycle Count: 5.8M
CPU Cycle Count: 354.4k
CPU Utilization (%): 5.9
Clock Rate (hz): 78.0M
Time (s): 77.3m
Ops/s: 159.4M
MACs/s: 75.9M
Inference/s: 12.9
Model Layers
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | # Ops | # MACs | Acc Cycles | CPU Cycles | Time (s) | Input Shape | Output Shape | Options |
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | quantize | 28.2k | 0 | 0 | 241.0k | 3.0m | 1x84x84x1 | 1x84x84x1 | Type=none |
| 1 | conv_2d | 2.2M | 968.2k | 1.9M | 11.0k | 23.7m | 1x84x84x1,16x3x3x1,16 | 1x82x82x16 | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 2 | max_pool_2d | 107.6k | 0 | 80.8k | 15.9k | 1.1m | 1x82x82x16 | 1x41x41x16 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 3 | conv_2d | 7.1M | 3.5M | 2.7M | 10.3k | 34.3m | 1x41x41x16,16x3x3x16,16 | 1x39x39x16 | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 4 | max_pool_2d | 23.1k | 0 | 17.4k | 15.8k | 300.0u | 1x39x39x16 | 1x19x19x16 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 5 | conv_2d | 2.7M | 1.3M | 1.0M | 10.3k | 13.0m | 1x19x19x16,32x3x3x16,32 | 1x17x17x32 | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 6 | max_pool_2d | 8.2k | 0 | 6.4k | 30.0k | 390.0u | 1x17x17x32 | 1x8x8x32 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 7 | reshape | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.7k | 120.0u | 1x8x8x32,2 | 1x2048 | Type=none |
| 8 | fully_connected | 131.2k | 65.5k | 98.5k | 2.2k | 1.3m | 1x2048,32x2048,32 | 1x32 | Activation:relu |
| 9 | fully_connected | 260.0 | 128.0 | 231.0 | 1.9k | 30.0u | 1x32,4x32,4 | 1x4 | Activation:none |
| 10 | softmax | 20.0 | 0 | 0 | 4.1k | 60.0u | 1x4 | 1x4 | Type=softmaxoptions |
| 11 | dequantize | 8.0 | 0 | 0 | 1.1k | 0 | 1x4 | 1x4 | Type=none |
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Model Diagram¶
mltk view rock_paper_scissors --tflite
Model Specification¶
# Bring in the required Keras classes
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Flatten, Dropout, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from mltk.core.model import (
MltkModel,
TrainMixin,
ImageDatasetMixin,
EvaluateClassifierMixin
)
# By default, we use the ParallelImageDataGenerator
# We could use the Keras ImageDataGenerator but it is slower
from mltk.core.preprocess.image.parallel_generator import ParallelImageDataGenerator
#from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# Import the dataset
from mltk.datasets.image import rock_paper_scissors_v2
# Instantiate the MltkModel object with the following 'mixins':
# - TrainMixin - Provides classifier model training operations and settings
# - ImageDatasetMixin - Provides image data generation operations and settings
# - EvaluateClassifierMixin - Provides classifier evaluation operations and settings
# @mltk_model # NOTE: This tag is required for this model be discoverable
class MyModel(
MltkModel,
TrainMixin,
ImageDatasetMixin,
EvaluateClassifierMixin
):
pass
my_model = MyModel()
#################################################
# General Settings
#
# For better tracking, the version should be incremented any time a non-trivial change is made
# NOTE: The version is optional and not used directly used by the MLTK
my_model.version = 1
# Provide a brief description about what this model models
# This description goes in the "description" field of the .tflite model file
my_model.description = 'Image classifier example for detecting Rock/Paper/Scissors hand gestures in images'
#################################################
# Training Settings
# This specifies the number of times we run the training
# samples through the model to update the model weights.
# Typically, a larger value leads to better accuracy at the expense of training time.
# Set to -1 to use the early_stopping callback and let the scripts
# determine how many epochs to train for (see below).
# Otherwise set this to a specific value (typically 40-200)
my_model.epochs = 125
# Specify how many samples to pass through the model
# before updating the training gradients.
# Typical values are 10-64
# NOTE: Larger values require more memory and may not fit on your GPU
my_model.batch_size = 32
# This specifies the algorithm used to update the model gradients
# during training. Adam is very common
# See https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers
my_model.optimizer = 'adam'
# List of metrics to be evaluated by the model during training and testing
my_model.metrics = ['accuracy']
# The "loss" function used to update the weights
# This is a classification problem with more than two labels so we use categorical_crossentropy
# See https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/losses
my_model.loss = 'categorical_crossentropy'
#################################################
# Training callback Settings
# Generate checkpoints every time the validation accuracy improves
# See https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/ModelCheckpoint
my_model.checkpoint['monitor'] = 'val_accuracy'
# https://keras.io/api/callbacks/reduce_lr_on_plateau/
# If the test loss doesn't improve after 'patience' epochs
# then decrease the learning rate by 'factor'
my_model.reduce_lr_on_plateau = dict(
monitor='loss',
factor = 0.95,
min_delta=0.001,
patience = 1
)
# If the accuracy doesn't improve after 35 epochs then stop training
# https://keras.io/api/callbacks/early_stopping/
my_model.early_stopping = dict(
monitor = 'accuracy',
patience = 25,
verbose=1
)
#################################################
# TF-Lite converter settings
my_model.tflite_converter['optimizations'] = ['DEFAULT']
# Tell the TfliteConverter to generated int8 weights/filters
my_model.tflite_converter['supported_ops'] = ['TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8']
# We want the input/output model data types to be float32
# since we're using samplewise_std_normalization=True during training
# With this, the TfliteConverter will automatically add quantize/dequantize
# layers to the model to automatically convert the float32 data to int8
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_input_type'] = 'float32'
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_output_type'] = 'float32'
# Generate a representative dataset from the validation data
my_model.tflite_converter['representative_dataset'] = 'generate'
#################################################
# Image Dataset Settings
# The directory of the training data
# NOTE: This can also be a directory path or a callback function
my_model.dataset = rock_paper_scissors_v2
# The classification type
my_model.class_mode = 'categorical'
# The class labels found in your training dataset directory
my_model.classes = rock_paper_scissors_v2.CLASSES
# The input shape to the model. The dataset samples will be resized if necessary
my_model.input_shape = (84,84,1)
# Shuffle the dataset directory once
my_model.shuffle_dataset_enabled = True
# The numbers of samples for each class is different
# Then ensures each class contributes equally to training the model
my_model.class_weights = 'balanced'
##################################################
# Image Classifier Settings
# These are parameters used by the image_classifier application
# They may be overridden by specifying similar options to the command:
# mltk classify_image rock_paper_scissors
# Minimum averaged model output threshold for a class to be considered detected, 0-255.
# Higher values increase precision at the cost of recall
my_model.model_parameters['detection_threshold'] = 175
# Controls the smoothing. Drop all inference results that are older than <now> minus window_duration.
# Longer durations (in milliseconds) will give a higher confidence that the results are correct, but may miss some images
my_model.model_parameters['average_window_duration_ms'] = 500
# The *minimum* number of inference results to average when calculating the detection value
my_model.model_parameters['minimum_count'] = 2
# Number of samples that should be different than the last detected sample before detecting again
my_model.model_parameters['suppression_count'] = 1
#################################################
# ParallelImageDataGenerator Settings
my_model.datagen = ParallelImageDataGenerator(
cores=0.65,
debug=False,
max_batches_pending=32,
validation_split= 0.15,
validation_augmentation_enabled=False,
rotation_range=15,
width_shift_range=5,
height_shift_range=5,
brightness_range=(0.80, 1.10),
contrast_range=(0.80, 1.10),
noise=['gauss', 'poisson', 's&p'],
zoom_range=(0.95, 1.05),
rescale=None,
horizontal_flip=True,
vertical_flip=True,
samplewise_center=True, # These settings require the model input to be float32
# NOTE: With these settings, the embedded device must also convert the images at runtime
samplewise_std_normalization=True,
)
#################################################
# Build the ML Model
# This model was adapted from:
# https://blog.keras.io/building-powerful-image-classification-models-using-very-little-data.html
#
# This defines the actual model layout using the Keras API.
# This particular model is a relatively standard
# sequential Convolution Neural Network (CNN).
#
# It is important to the note the usage of the
# "model" argument.
# Rather than hardcode values, the model is
# used to build the model, e.g.:
# Dense(model.n_classes)
#
# This way, the various model properties above can be modified
# without having to re-write this section.
def my_model_builder(model: MyModel):
keras_model = Sequential()
# Increasing this value can increase model accuracy
# at the expense of more RAM and execution latency
filter_count = 16
# "Feature Learning" layers
keras_model.add(Conv2D(filter_count, (3, 3), input_shape=model.input_shape))
keras_model.add(Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
keras_model.add(Conv2D(filter_count, (3, 3)))
keras_model.add(Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
keras_model.add(Conv2D(filter_count*2, (3, 3)))
keras_model.add(Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
# "Classification" layers
keras_model.add(Flatten()) # this converts our 3D feature maps to 1D feature vectors
keras_model.add(Dense(filter_count*2)) # This should be the same size at the previous Conv2D layer count
keras_model.add(Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(Dropout(0.5))
keras_model.add(Dense(model.n_classes, activation='softmax'))
keras_model.compile(
loss=model.loss,
optimizer=model.optimizer,
metrics=model.metrics
)
return keras_model
my_model.build_model_function = my_model_builder
# Register the "dump" custom command
import typer
@my_model.cli.command('dump')
def dump_custom_command(
count:int = typer.Option(100, '--count',
help='Number of samples to dump'
),
):
"""Custom command to dump the augmented samples
\b
Invoke this command with:
mltk custom rock_paper_scissors dump --count 20
"""
my_model.datagen.save_to_dir = my_model.create_log_dir('dump', delete_existing=True)
my_model.datagen.debug = True
my_model.datagen.cores = 1
my_model.datagen.max_batches_pending = 1
my_model.datagen.batch_size = 1
my_model.load_dataset(subset='training')
for i, _ in enumerate(my_model.x):
if i >= count:
break
my_model.unload_dataset()
print(f'Generated data dump to: {my_model.datagen.save_to_dir}')
##########################################################################################
# The following allows for running this model training script directly, e.g.:
# python rock_paper_scissors.py
#
# Note that this has the same functionality as:
# mltk train rock_paper_scissors
#
if __name__ == '__main__':
import mltk.core as mltk_core
from mltk import cli
# Setup the CLI logger
cli.get_logger(verbose=False)
# If this is true then this will do a "dry run" of the model testing
# If this is false, then the model will be fully trained
test_mode_enabled = True
# Train the model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk train rock_paper_scissors-test --clean
train_results = mltk_core.train_model(my_model, clean=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(train_results)
# Evaluate the model against the quantized .h5 (i.e. float32) model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk evaluate rock_paper_scissors-test
tflite_eval_results = mltk_core.evaluate_model(my_model, verbose=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(tflite_eval_results)
# Profile the model in the simulator
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk profile rock_paper_scissors-test
profiling_results = mltk_core.profile_model(my_model, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(profiling_results)