keyword_spotting_pacman_v2¶
Source code: keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.py
Pre-trained model: keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.mltk.zip
This model is a CNN classifier to detect the keywords:
left
right
up
down
stop
go
It is specially trained to handle the background noise generated by the video game “Pac-Man”.
This model specification script is designed to work with the Keyword Spotting Pac-Man tutorial.
Training the Model¶
This model uses Knowledge Distallation.
The basic idea behind knowledge distallation is:
Train a large (aka “teacher”) model that gets good accuracy
Train smaller (aka “student”) model with the guidance of the “teacher” model
In this way, the “student” model can more efficiently learn the important features of the dataset and get similar accuracy to the much larger “teacher” model.
To train the teacher model, define the environment variable TRAIN_TEACHER=1 then train:
export TRAIN_TEACHER=1
mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
This will generate the file: keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5 in the same directory as the current file.
This is the teacher model in the Keras HDF5 format.
Once the teacher is trained, the “student” model (the model that is programmed to the embedded device) is
trained by defining the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER=0, e.g.:
export TRAIN_TEACHER=0
mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
When training the student model, the keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5 will be loaded and used during model training.
Changes from v1¶
The following changes have been made from the original keyword_spotting_pacman model:
Cleaned the
mltk.datasets.audio.speech_commands.speech_commands_v2dataset by removing invalid samplesThis gives the most improvement
Knowledge distillation
Phase 1: Train a large model that gets good accuracy
Phase 2: Train smaller with the guidance of the larger model
The smaller leverages the knowledge of the larger
More details at Knowledge Distallation
Increased the size of the model
Previously, a smaller model that executed in 40ms was used, and several inferences were averaged
Now, a larger model that executes in 90ms and no averaging
This helps to make the Pac-Man game more responsive
Increased the size of the “unknown” class
The number of “unknown” samples is 4x the number of a “known” class
Added cropped “known” samples to the “unknown” class
This way the model only triggers on fully buffered keywords, not partial words as they’re streaming in
Added better background noise
Sounds of crowds, conferences, etc.
Added BRD2601 background noise to all samples
The dev board microphone has a low frequency “hum”; this was recorded and added to all the training samples so they “look” closer to what would be seen at runtime
Re-enabled the Microfrontend Noise Reduction block
This was found to greatly help with generating clean spectrograms at runtime
During training, each sample is padded with an extra 1s of background noise so that the noise reduction block properly “warms up” before the actual keyword streams in. The padding is then removed in the resulting spectrogram
Dataset¶
This uses the mltk.datasets.audio.speech_commands.speech_commands_v2 dataset provided by Google.
Plus an additional background noise recorded when play the video game “Pac-Man”.
Preprocessing¶
This uses the mltk.core.preprocess.audio.audio_feature_generator.AudioFeatureGenerator with the
mltk.core.preprocess.audio.audio_feature_generator.AudioFeatureGenerator settings:
sample_rate: 16kHz
sample_length: 1000ms
window size: 20ms
window step: 10ms
n_channels: 68
Commands¶
# Do a "dry run" test training of the "teacher" model
export TRAIN_TEACHER=1
mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2-test
# Train the "teacher" model
export TRAIN_TEACHER=1
mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
# Train the "student" model
export TRAIN_TEACHER=0
mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
# Evaluate the trained model .tflite model
mltk evaluate keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --tflite
# Profile the model in the MVP hardware accelerator simulator
mltk profile keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --accelerator MVP
# Profile the model on a physical development board
mltk profile keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --accelerator MVP --device
# Run the model in the audio classifier on the local PC
mltk classify_audio keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --verbose
# Run the model in the audio classifier on the physical device
mltk classify_audio keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --device --verbose
Model Summary¶
mltk summarize keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --tflite
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | Input(s) | Output(s) | Config |
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | conv_2d | 99x68x1 (int8) | 99x68x10 (int8) | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x1 (int8) | | |
| | | 10 (int32) | | |
| 1 | max_pool_2d | 99x68x10 (int8) | 49x34x10 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 2 | conv_2d | 49x34x10 (int8) | 49x34x20 (int8) | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x10 (int8) | | |
| | | 20 (int32) | | |
| 3 | max_pool_2d | 49x34x20 (int8) | 24x17x20 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 4 | conv_2d | 24x17x20 (int8) | 24x17x40 (int8) | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x20 (int8) | | |
| | | 40 (int32) | | |
| 5 | max_pool_2d | 24x17x40 (int8) | 12x8x40 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 6 | conv_2d | 12x8x40 (int8) | 12x8x40 (int8) | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x40 (int8) | | |
| | | 40 (int32) | | |
| 7 | max_pool_2d | 12x8x40 (int8) | 6x4x40 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 8 | conv_2d | 6x4x40 (int8) | 6x4x20 (int8) | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x40 (int8) | | |
| | | 20 (int32) | | |
| 9 | max_pool_2d | 6x4x20 (int8) | 1x4x20 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x6 filter:1x6 activation:none |
| 10 | reshape | 1x4x20 (int8) | 80 (int8) | Type=none |
| | | 2 (int32) | | |
| 11 | fully_connected | 80 (int8) | 7 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 80 (int8) | | |
| | | 7 (int32) | | |
| 12 | softmax | 7 (int8) | 7 (int8) | Type=softmaxoptions |
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Total MACs: 8.098 M
Total OPs: 16.436 M
Name: keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
Version: 1
Description: Keyword spotting classifier to detect: left, right, up, down, stop, go with Pac-Man video game background noise
Classes: left, right, up, down, stop, go, _unknown_
Runtime memory size (RAM): 87.460 k
hash: c536b6f6dd07177d0ea769829f66623d
date: 2022-10-21T16:10:51.603Z
fe.sample_rate_hz: 16000
fe.fft_length: 512
fe.sample_length_ms: 1000
fe.window_size_ms: 20
fe.window_step_ms: 10
fe.filterbank_n_channels: 68
fe.filterbank_upper_band_limit: 8000.0
fe.filterbank_lower_band_limit: 125.0
fe.noise_reduction_enable: True
fe.noise_reduction_smoothing_bits: 10
fe.noise_reduction_even_smoothing: 0.02500000037252903
fe.noise_reduction_odd_smoothing: 0.05999999865889549
fe.noise_reduction_min_signal_remaining: 0.029999999329447746
fe.pcan_enable: False
fe.pcan_strength: 0.949999988079071
fe.pcan_offset: 80.0
fe.pcan_gain_bits: 21
fe.log_scale_enable: True
fe.log_scale_shift: 6
fe.activity_detection_enable: False
fe.activity_detection_alpha_a: 0.5
fe.activity_detection_alpha_b: 0.800000011920929
fe.activity_detection_arm_threshold: 0.75
fe.activity_detection_trip_threshold: 0.800000011920929
fe.dc_notch_filter_enable: True
fe.dc_notch_filter_coefficient: 0.949999988079071
fe.quantize_dynamic_scale_enable: True
fe.quantize_dynamic_scale_range_db: 40.0
average_window_duration_ms: 100
detection_threshold_list: [242, 242, 239, 239, 252, 252, 255]
suppression_ms: 1000
minimum_count: 1
volume_gain: 0.0
latency_ms: 10
verbose_model_output_logs: False
.tflite file size: 45.9kB
Model Profiling Report¶
# Profile on physical EFR32xG24 using MVP accelerator
mltk profile keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --device --accelerator MVP
Profiling Summary
Name: keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
Accelerator: MVP
Input Shape: 1x99x68x1
Input Data Type: int8
Output Shape: 1x7
Output Data Type: int8
Flash, Model File Size (bytes): 45.9k
RAM, Runtime Memory Size (bytes): 91.2k
Operation Count: 16.7M
Multiply-Accumulate Count: 8.1M
Layer Count: 13
Unsupported Layer Count: 0
Accelerator Cycle Count: 6.5M
CPU Cycle Count: 280.4k
CPU Utilization (%): 4.3
Clock Rate (hz): 78.0M
Time (s): 83.8m
Ops/s: 198.8M
MACs/s: 96.4M
Inference/s: 11.9
Model Layers
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | # Ops | # MACs | Acc Cycles | CPU Cycles | Time (s) | Input Shape | Output Shape | Options |
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | conv_2d | 1.4M | 605.9k | 965.6k | 30.3k | 12.4m | 1x99x68x1,10x3x3x1,10 | 1x99x68x10 | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 1 | max_pool_2d | 66.6k | 0 | 50.0k | 10.2k | 720.0u | 1x99x68x10 | 1x49x34x10 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 2 | conv_2d | 6.1M | 3.0M | 2.3M | 30.1k | 29.1m | 1x49x34x10,20x3x3x10,20 | 1x49x34x20 | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 3 | max_pool_2d | 32.6k | 0 | 24.6k | 19.0k | 420.0u | 1x49x34x20 | 1x24x17x20 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 4 | conv_2d | 5.9M | 2.9M | 2.1M | 30.2k | 26.8m | 1x24x17x20,40x3x3x20,40 | 1x24x17x40 | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 5 | max_pool_2d | 15.4k | 0 | 11.8k | 36.5k | 480.0u | 1x24x17x40 | 1x12x8x40 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 6 | conv_2d | 2.8M | 1.4M | 916.8k | 30.2k | 11.7m | 1x12x8x40,40x3x3x40,40 | 1x12x8x40 | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 7 | max_pool_2d | 3.8k | 0 | 3.2k | 36.5k | 450.0u | 1x12x8x40 | 1x6x4x40 | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 8 | conv_2d | 347.0k | 172.8k | 100.6k | 30.2k | 1.4m | 1x6x4x40,20x3x3x40,20 | 1x6x4x20 | Padding:same stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| 9 | max_pool_2d | 480.0 | 0 | 460.0 | 18.7k | 240.0u | 1x6x4x20 | 1x1x4x20 | Padding:valid stride:1x6 filter:1x6 activation:none |
| 10 | reshape | 0 | 0 | 0 | 860.0 | 30.0u | 1x1x4x20,2 | 1x80 | Type=none |
| 11 | fully_connected | 1.1k | 560.0 | 899.0 | 2.2k | 30.0u | 1x80,7x80,7 | 1x7 | Activation:none |
| 12 | softmax | 35.0 | 0 | 0 | 5.4k | 60.0u | 1x7 | 1x7 | Type=softmaxoptions |
+-------+-----------------+--------+--------+------------+------------+----------+-------------------------+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
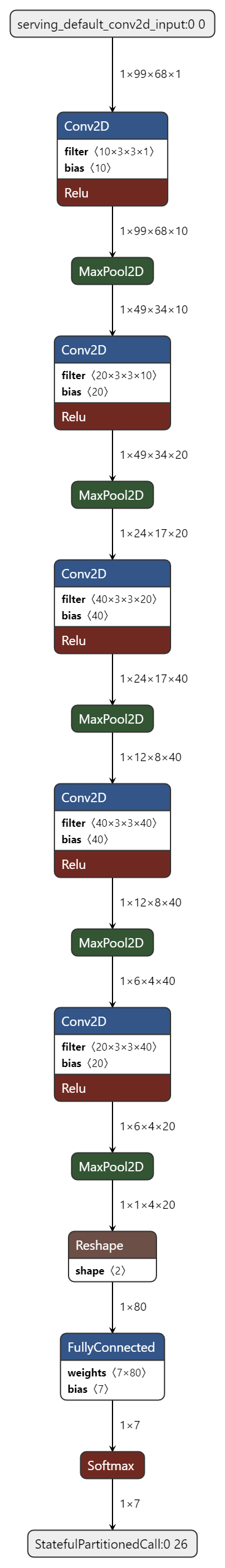
Model Diagram¶
mltk view keyword_spotting_pacman_v2 --tflite
Model Specification¶
# Import the Tensorflow packages
# required to build the model layout
import os
import warnings
import shutil
import logging
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import mltk.core as mltk_core
# Import the Google speech_commands dataset package
# This manages downloading and extracting the dataset
from mltk.datasets.audio.speech_commands import speech_commands_v2
# Import the AudioFeatureGeneratorSettings which we'll configure
from mltk.core.preprocess.audio.audio_feature_generator import AudioFeatureGeneratorSettings
from mltk.core.preprocess.utils import tf_dataset as tf_dataset_utils
from mltk.core.preprocess.utils import audio as audio_utils
from mltk.core.preprocess.utils import image as image_utils
from mltk.utils.python import install_pip_package
from mltk.utils.archive_downloader import download_verify_extract, download_url
from mltk.core.keras.models import KnowledgeDistillationModel
##########################################################################
# Instantiate the MltkModel instance
#
# @mltk_model
class MyModel(
mltk_core.MltkModel, # We must inherit the MltkModel class
mltk_core.TrainMixin, # We also inherit the TrainMixin since we want to train this model
mltk_core.DatasetMixin, # We also need the DatasetMixin mixin to provide the relevant dataset properties
mltk_core.EvaluateClassifierMixin, # While not required, also inherit EvaluateClassifierMixin to help will generating evaluation stats for our classification model
mltk_core.SshMixin,
):
pass
my_model = MyModel()
#################################################
# General Settings
# For better tracking, the version should be incremented any time a non-trivial change is made
# NOTE: The version is optional and not used directly used by the MLTK
my_model.version = 1
# Provide a brief description about what this model models
# This description goes in the "description" field of the .tflite model file
my_model.description = 'Keyword spotting classifier to detect: left, right, up, down, stop, go with Pac-Man video game background noise'
#################################################
# Training Basic Settings
# This specifies the number of times we run the training
# samples through the model to update the model weights.
# Typically, a larger value leads to better accuracy at the expense of training time.
# Otherwise set this to a specific value (typically 40-200)
my_model.epochs = 100
# Specify how many samples to pass through the model
# before updating the training gradients.
# Typical values are 10-64
# NOTE: Larger values require more memory and may not fit on your GPU
my_model.batch_size = 24
##########################################################################
# Define the model architecture
#
def my_teacher_model_builder(model: MyModel) -> tf.keras.Model:
"""Build the "Teacher" Keras model
This is used when the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER=1
This is called by the MLTK just before "teacher" training starts.
See https://keras.io/examples/vision/knowledge_distillation/ for more details.
Arguments:
my_model: The MltkModel instance
Returns:
Compiled Keras model instance
"""
input_shape = model.input_shape
filters = 32
keras_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(name=model.name +'-teacher')
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, (3,3), padding='same', input_shape=input_shape))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*2, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*4, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*4, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*4, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(keras_model.layers[-1].output_shape[1],1)))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(model.n_classes, activation='softmax'))
keras_model.compile(
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics= ['accuracy']
)
return keras_model
def my_teacher_model_saver(
mltk_model:mltk_core.MltkModel,
keras_model:tf.keras.Model,
logger:logging.Logger
) -> tf.keras.Model:
"""Save the teacher model
This is called just after model training completes.
This copies the keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5
model file to same directory as the current python script.
This is used when the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER=1
"""
teacher_h5_path = get_teacher_h5_path(check_exists=False)
logger.debug(f'Saving {teacher_h5_path}')
keras_model.save(teacher_h5_path, save_format='tf')
return keras_model
def my_student_model_builder(model: MyModel) -> tf.keras.Model:
"""Build the "Student" Keras model
This is called by the MLTK just before training starts.
This is used when the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER=0
See https://keras.io/examples/vision/knowledge_distillation/ for more details.
Arguments:
my_model: The MltkModel instance
Returns:
Compiled Keras model instance
"""
input_shape = model.input_shape
filters = 10
keras_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(name=model.name + '-student')
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, (3,3), padding='same', input_shape=input_shape))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*2, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*4, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*4, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(2,2))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters*2, (3,3), padding='same',))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(keras_model.layers[-1].output_shape[1],1)))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.3))
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
keras_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(model.n_classes, activation='softmax'))
keras_model.compile(
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics= ['accuracy']
)
# Load the previously saved "teacher" keras model
teacher_h5_path = get_teacher_h5_path(try_archive=True)
teacher_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(teacher_h5_path, compile=True)
distiller = KnowledgeDistillationModel(student=keras_model, teacher=teacher_model)
distiller.compile(
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'],
student_loss_fn=tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(),
distillation_loss_fn=tf.keras.losses.KLDivergence(),
alpha=0.1,
temperature=10,
)
return distiller
def my_student_model_saver(
mltk_model:mltk_core.MltkModel,
keras_model:tf.keras.Model,
logger:logging.Logger
) -> tf.keras.Model:
"""Save the student model
This is called just after model training completes.
This discards the KnowledgeDistillationModel and only saves the student model
This is used when the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER=0
"""
# Discard the KnowledgeDistillationModel and only save the student model
student_model = keras_model.student
# Also add the keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5 to the training output directory
# This way the teacher model is added to the model archive
teacher_h5_path = get_teacher_h5_path()
h5_path = mltk_model.h5_log_dir_path
shutil.copy(teacher_h5_path, f'{os.path.dirname(h5_path)}/{os.path.basename(teacher_h5_path)}')
return student_model
##########################################################################
# Training callback Settings
#
# The MLTK enables the tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint by default.
my_model.checkpoint['monitor'] = 'val_accuracy'
# https://keras.io/api/callbacks/reduce_lr_on_plateau/
# If the test accuracy doesn't improve after 'patience' epochs
# then decrease the learning rate by 'factor'
my_model.reduce_lr_on_plateau = dict(
monitor='accuracy',
factor = 0.95,
patience = 1,
min_delta=0.01
)
# https://keras.io/api/callbacks/early_stopping/
# If the validation student loss doesn't improve after 'patience' epochs then stop training
my_model.early_stopping = dict(
monitor='val_student_loss',
mode='min',
verbose=1,
patience=50,
min_delta=0.0001
)
# https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard
# my_model.tensorboard = dict(
# histogram_freq=0, # frequency (in epochs) at which to compute activation and weight histograms
# # for the layers of the model. If set to 0, histograms won't be computed.
# # Validation data (or split) must be specified for histogram visualizations.
# write_graph=False, # whether to visualize the graph in TensorBoard. The log file can become quite large when write_graph is set to True.
# write_images=False, # whether to write model weights to visualize as image in TensorBoard.
# update_freq="batch", # 'batch' or 'epoch' or integer. When using 'batch', writes the losses and metrics
# # to TensorBoard after each batch. The same applies for 'epoch'.
# # If using an integer, let's say 1000, the callback will write the metrics and losses
# # to TensorBoard every 1000 batches. Note that writing too frequently to
# # TensorBoard can slow down your training.
# profile_batch=(51,51), # Profile the batch(es) to sample compute characteristics.
# # profile_batch must be a non-negative integer or a tuple of integers.
# # A pair of positive integers signify a range of batches to profile.
# # By default, it will profile the second batch. Set profile_batch=0 to disable profiling.
# )
# NOTE: You can also add manually add other KerasCallbacks
# https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/
# Any callbacks specified here will override the built-in callbacks
# (e.g. my_model.reduce_lr_on_plateau, my_model.early_stopping)
my_model.train_callbacks = [
tf.keras.callbacks.TerminateOnNaN()
]
##########################################################################
# Specify AudioFeatureGenerator Settings
# See https://siliconlabs.github.io/mltk/docs/audio/audio_feature_generator.html
#
frontend_settings = AudioFeatureGeneratorSettings()
frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz = 16000
frontend_settings.sample_length_ms = 1000
frontend_settings.window_size_ms = 20
frontend_settings.window_step_ms = 10
frontend_settings.filterbank_n_channels = 68
frontend_settings.filterbank_upper_band_limit = frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz/2
frontend_settings.filterbank_lower_band_limit = 125.0 # The dev board mic seems to have a lot of noise at lower frequencies
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_enable = True
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_smoothing_bits = 10
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_even_smoothing = 0.025
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_odd_smoothing = 0.06
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_min_signal_remaining = 0.03
frontend_settings.pcan_enable = False # Disable the PCAN block
frontend_settings.log_scale_enable = True
frontend_settings.log_scale_shift = 6
frontend_settings.dc_notch_filter_enable = True # Enable the DC notch filter
frontend_settings.dc_notch_filter_coefficient = 0.95
frontend_settings.quantize_dynamic_scale_enable = True # Enable dynamic quantization
frontend_settings.quantize_dynamic_scale_range_db = 40.0
# Add the Audio Feature generator settings to the model parameters
# This way, they are included in the generated .tflite model file
# See https://siliconlabs.github.io/mltk/docs/guides/model_parameters.html
my_model.model_parameters.update(frontend_settings)
##########################################################################
# Specify the other dataset settings
#
my_model.input_shape = frontend_settings.spectrogram_shape + (1,)
# Add the direction keywords plus a _unknown_ meta class
my_model.classes = ['left', 'right', 'up', 'down', 'stop', 'go', '_unknown_']
# Ensure the class weights are balanced during training
# https://towardsdatascience.com/why-weight-the-importance-of-training-on-balanced-datasets-f1e54688e7df
my_model.class_weights = 'balanced'
validation_split = 0.2
# We want the "unknown" samples to be 4x the number of other samples
unknown_class_multiplier = 4.0
# Uncomment this to dump the augmented audio samples to the log directory
#data_dump_dir = my_model.create_log_dir('dataset_dump')
##########################################################################
# Create the audio augmentation pipeline
#
# Install the other 3rd party packages required from preprocessing
install_pip_package('audiomentations')
install_pip_package('noisereduce')
install_pip_package('pyloudnorm')
import librosa
import audiomentations
import noisereduce
import pyloudnorm
def audio_augmentation_pipeline(
path_batch:np.ndarray,
label_batch:np.ndarray,
seed:np.ndarray
) -> np.ndarray:
"""Augment a batch of audio clips and generate spectrograms
This does the following, for each audio file path in the input batch:
1. Read audio file
2. Adjust its length to fit within the specified length
3. Apply random augmentations to the audio sample using audiomentations
4. Convert to the specified sample rate (if necessary)
5. Generate a spectrogram from the augmented audio sample
6. Dump the augmented audio and spectrogram (if necessary)
NOTE: This will be execute in parallel across *separate* subprocesses.
Arguments:
path_batch: Batch of audio file paths
label_batch: Batch of corresponding labels
seed: Batch of seeds to use for random number generation,
This ensures that the "random" augmentations are reproducible
Return:
Generated batch of spectrograms from augmented audio samples
"""
batch_length = path_batch.shape[0]
height, width = frontend_settings.spectrogram_shape
x_shape = (batch_length, height, width, 1)
x_batch = np.empty(x_shape, dtype=np.int8)
# This is the amount of padding we add to the beginning of the sample
# This allows for "warming up" the noise reduction block
padding_length_ms = 1000
padded_frontend_settings = frontend_settings.copy()
padded_frontend_settings.sample_length_ms += padding_length_ms
# For each audio sample path in the current batch
for i, (audio_path, labels) in enumerate(zip(path_batch, label_batch)):
class_id = np.argmax(labels)
np.random.seed(seed[i])
rn = np.random.random()
use_cropped_sample_as_unknown = False
using_silence_as_unknown = False
# class_id=6 is the "unknown" class
# 35% of the time we want to replace this sample
# either either silence or a cropped "known" sample
if class_id == 6 and rn < 0.35:
# 5% of the time we want to replace an "unknown" sample with silence
if rn < .05:
using_silence_as_unknown = True
original_sample_rate = 16000
sample = np.zeros((original_sample_rate,), dtype=np.float32)
else:
# Otherwise, find a "known" sample in the current batch
# Later, we'll crop this sample and use it as an "unknown" sample
choices = list(range(batch_length))
np.random.shuffle(choices)
for choice_index in choices:
if np.argmax(label_batch[choice_index]) == 6:
continue
audio_path = path_batch[choice_index]
use_cropped_sample_as_unknown = True
break
if not using_silence_as_unknown:
# Read the audio file
sample, original_sample_rate = audio_utils.read_audio_file(
audio_path,
return_sample_rate=True,
return_numpy=True
)
# Normalize the sample's volume
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
sample = pyloudnorm.normalize.peak(sample, 0.0)
sample = noisereduce.reduce_noise(
y=sample,
sr=original_sample_rate,
stationary=True
)
# Crop the first 50ms of the sample
# as it was found that many of the samples in the dataset
# have mouse clicking at the beginning
sample = sample[int(original_sample_rate*.050):]
# Create a buffer to hold the padded sample
padding_length = int((original_sample_rate * padding_length_ms) / 1000)
padded_sample_length = int((original_sample_rate * padded_frontend_settings.sample_length_ms) / 1000)
padded_sample = np.zeros((padded_sample_length,), dtype=np.float32)
# If we want to crop a "known" sample and use it as an unknown sample
if use_cropped_sample_as_unknown:
# Trim any silence from the sample
trimmed_sample, _ = librosa.effects.trim(sample, top_db=15)
# Randomly insert 30% to 50% of the trimmed sample into padded sample buffer
# Note that the entire trimmed sample is actually added to the padded sample buffer
# However, only the part of the sample that is after padding_length_ms will actually be used.
# Everything before will eventually be dropped
trimmed_sample_length = len(trimmed_sample)
cropped_sample_percent = 1.0 - np.random.uniform(.3, .5)
cropped_sample_length = int(trimmed_sample_length * cropped_sample_percent)
cropped_sample_offset = padding_length - cropped_sample_length
padded_sample[cropped_sample_offset:cropped_sample_offset+trimmed_sample_length] += trimmed_sample
else:
# Otherwise, adjust the audio clip to the length defined in the frontend_settings
out_length = int((original_sample_rate * frontend_settings.sample_length_ms) / 1000)
sample = audio_utils.adjust_length(
sample,
out_length=out_length,
trim_threshold_db=30,
offset=np.random.uniform(0, 1)
)
padded_sample[padding_length:padding_length+len(sample)] += sample
# Initialize the global audio augmentations instance
# NOTE: We want this to be global so that we only initialize it once per subprocess
audio_augmentations = globals().get('audio_augmentations', None)
if audio_augmentations is None:
dataset_dir = speech_commands_v2.load_clean_data()
audio_augmentations = audiomentations.Compose(
p=1.0,
transforms=[
#audiomentations.PitchShift(min_semitones=-1, max_semitones=1, p=0.5),
audiomentations.TimeStretch(min_rate=0.90, max_rate=1.1, p=1.0),
audiomentations.Gain(min_gain_in_db=0.95, max_gain_in_db=1.5, p=1.0),
audiomentations.AddBackgroundNoise(
f'{dataset_dir}/_background_noise_/brd2601',
min_absolute_rms_in_db=-75.0,
max_absolute_rms_in_db=-60.0,
noise_rms="absolute",
lru_cache_size=50,
p=1.0
),
audiomentations.AddBackgroundNoise(
f'{dataset_dir}/_background_noise_/pacman',
min_absolute_rms_in_db=-60,
max_absolute_rms_in_db=-35,
noise_rms="absolute",
lru_cache_size=50,
p=0.60
),
audiomentations.AddBackgroundNoise(
f'{dataset_dir}/_background_noise_/ambient',
min_absolute_rms_in_db=-70,
max_absolute_rms_in_db=-30,
noise_rms="absolute",
lru_cache_size=50,
p=0.60
),
audiomentations.AddGaussianSNR(min_snr_in_db=30, max_snr_in_db=60, p=0.25),
])
globals()['audio_augmentations'] = audio_augmentations
# Apply random augmentations to the audio sample
augmented_sample = audio_augmentations(padded_sample, original_sample_rate)
# Convert the sample rate (if necessary)
if original_sample_rate != frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz:
augmented_sample, _ = audio_utils.resample(
augmented_sample,
orig_sr=original_sample_rate,
target_sr=frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz
)
# Ensure the sample values are within (-1,1)
augmented_sample = np.clip(augmented_sample, -1.0, 1.0)
# Generate a spectrogram from the augmented audio sample
spectrogram = audio_utils.apply_frontend(
sample=augmented_sample,
settings=padded_frontend_settings,
dtype=np.int8
)
# The input audio sample was padded with padding_length_ms of background noise
# Drop the background noise from the final spectrogram used for training
spectrogram = spectrogram[-height:, :]
# The output spectrogram is 2D, add a channel dimension to make it 3D:
# (height, width, channels=1)
spectrogram = np.expand_dims(spectrogram, axis=-1)
x_batch[i] = spectrogram
# Dump the augmented audio sample AND corresponding spectrogram (if necessary)
data_dump_dir = globals().get('data_dump_dir', None)
if data_dump_dir:
try:
from cv2 import cv2
except:
import cv2
fn = os.path.basename(audio_path.decode('utf-8'))
audio_dump_path = f'{data_dump_dir}/{class_id}-{fn[:-4]}-{seed[0]}.wav'
spectrogram_dumped = np.squeeze(spectrogram, axis=-1)
# Transpose to put the time on the x-axis
spectrogram_dumped = np.transpose(spectrogram_dumped)
# Convert from int8 to uint8
spectrogram_dumped = np.clip(spectrogram_dumped +128, 0, 255)
spectrogram_dumped = spectrogram_dumped.astype(np.uint8)
# Increase the size of the spectrogram to make it easier to see as a jpeg
spectrogram_dumped = cv2.resize(spectrogram_dumped, (height*3,width*3))
audio_dump_path = audio_utils.write_audio_file(
audio_dump_path,
augmented_sample,
sample_rate=frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz
)
image_dump_path = audio_dump_path.replace('.wav', '.jpg')
jpg_data = cv2.applyColorMap(spectrogram_dumped, cv2.COLORMAP_HOT)
cv2.imwrite(image_dump_path, jpg_data)
return x_batch
##########################################################################
# Define the MltkDataset object
# NOTE: This class is optional but is useful for organizing the code
#
class MyDataset(mltk_core.MltkDataset):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.pools = []
def load_dataset(
self,
subset: str,
test:bool = False,
**kwargs
) -> Tuple[tf.data.Dataset, None, tf.data.Dataset]:
"""Load the dataset subset
This is called automatically by the MLTK before training
or evaluation.
Args:
subset: The dataset subset to return: 'training' or 'evaluation'
test: This is optional, it is used when invoking a training "dryrun", e.g.: mltk train audio_tf_dataset-test
If this is true, then only return a small portion of the dataset for testing purposes
Return:
if subset == training:
A tuple, (train_dataset, None, validation_dataset)
else:
validation_dataset
"""
if subset == 'training':
x = self.load_subset('training', test=test)
validation_data = self.load_subset('validation', test=test)
return x, None, validation_data
else:
x = self.load_subset('validation', test=test)
return x
def unload_dataset(self):
"""Unload the dataset by shutting down the processing pools"""
for pool in self.pools:
pool.shutdown()
self.pools.clear()
def load_subset(self, subset:str, test:bool) -> tf.data.Dataset:
"""Load the subset"""
if subset in ('validation', 'evaluation'):
split = (0, validation_split)
elif subset == 'training':
split = (validation_split, 1)
data_dump_dir = globals().get('data_dump_dir', None)
if data_dump_dir:
print(f'\n\n*** Dumping augmented samples to: {data_dump_dir}\n\n')
else:
split = None
my_model.class_counts = {}
# Download, extract, and clean the "Speech Commands" dataset
dataset_dir = speech_commands_v2.load_clean_data()
dataset_background_dir = f'{dataset_dir}/_background_noise_'
# Download the Pac-Man video game audio and add it to the _background_noise_/pacman of the dataset
pacman_background_noise_dst_path = f'{dataset_background_dir}/pacman/recorded_pacman_game_play.wav'
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(pacman_background_noise_dst_path), exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(pacman_background_noise_dst_path):
pacman_background_noise_dir = download_verify_extract(
url='https://github.com/SiliconLabs/mltk_assets/raw/master/datasets/recorded_pacman_game_play.7z',
dest_subdir='datasets/recorded_pacman_game_play',
file_hash='749F552BC2ABA11E618969D8B0F6E5BDD62AC7A2',
show_progress=False,
remove_root_dir=False
)
pacman_background_noise_src_path = f'{pacman_background_noise_dir}/{os.path.basename(pacman_background_noise_dst_path)}'
shutil.copy(pacman_background_noise_src_path, pacman_background_noise_dst_path)
# Download the BRD2601 background microphone audio and add it to the _background_noise_/brd2601 of the dataset
brd2601_background_noise_dst_path = f'{dataset_dir}/_background_noise_/brd2601/brd2601_background_audio.wav'
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(brd2601_background_noise_dst_path), exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(brd2601_background_noise_dst_path):
background_noise_dir = download_verify_extract(
url='https://github.com/SiliconLabs/mltk_assets/raw/master/datasets/brd2601_background_audio.7z',
dest_subdir='datasets/brd2601_background_audio',
file_hash='3069A85002965A7830C660343C215EDD4FAE39C6',
show_progress=False,
remove_root_dir=False
)
background_noise_src_path = f'{background_noise_dir}/{os.path.basename(brd2601_background_noise_dst_path)}'
shutil.copy(background_noise_src_path, brd2601_background_noise_dst_path)
# Download other ambient background audio and add it to the _background_noise_/ambient of the dataset
URLS = [
'https://assets.mixkit.co/sfx/download/mixkit-very-crowded-pub-or-party-loop-360.wav',
'https://www.soundjay.com/human/crowd-talking-1.wav',
'https://assets.mixkit.co/sfx/download/mixkit-big-crowd-talking-loop-364.wav',
'https://assets.mixkit.co/sfx/download/mixkit-restaurant-crowd-talking-ambience-444.wav',
]
for url in URLS:
fn = os.path.basename(url)
dst_path = f'{dataset_background_dir}/ambient/{fn}'
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(dst_path), exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(dst_path):
download_url(url=url, dst_path=dst_path)
sample, original_sample_rate = audio_utils.read_audio_file(
dst_path,
return_sample_rate=True,
return_numpy=True
)
sample = audio_utils.resample(
sample,
orig_sr=original_sample_rate,
target_sr=frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz
)
audio_utils.write_audio_file(dst_path, sample, sample_rate=16000)
# Create a tf.data.Dataset from the extracted "Speech Commands" directory
max_samples_per_class = my_model.batch_size if test else -1
class_counts = my_model.class_counts[subset] if subset else my_model.class_counts
features_ds, labels_ds = tf_dataset_utils.load_audio_directory(
directory=dataset_dir,
classes=my_model.classes,
onehot_encode=True, # We're using categorical cross-entropy so one-hot encode the labels
shuffle=True,
seed=42,
max_samples_per_class=max_samples_per_class,
split=split,
unknown_class_percentage=unknown_class_multiplier,
return_audio_data=False, # We only want to return the file paths
class_counts=class_counts,
list_valid_filenames_in_directory_function=speech_commands_v2.list_valid_filenames_in_directory
)
# We use an incrementing counter as the seed for the random augmentations
# This helps to keep the training reproducible
seed_counter = tf.data.experimental.Counter()
features_ds = features_ds.zip((features_ds, labels_ds, seed_counter))
if subset:
# Usage of tf_dataset_utils.parallel_process()
# is optional, but can speed-up training as the data augmentations
# are spread across the available CPU cores.
# Each CPU core gets its own subprocess,
# and and subprocess executes audio_augmentation_pipeline() on batches of the dataset.
per_job_batch_size = my_model.batch_size * 100
features_ds = features_ds.batch(per_job_batch_size // 100, drop_remainder=True)
features_ds, pool = tf_dataset_utils.parallel_process(
features_ds,
audio_augmentation_pipeline,
dtype=np.int8,
#n_jobs=72 if subset == 'training' else 32, # These are the settings for a 128 CPU core cloud machine
#n_jobs=44 if subset == 'training' else 16, # These are the settings for a 96 CPU core cloud machine
#n_jobs=36 if subset == 'training' else 18, # These are the settings for a 64 CPU core cloud machine
n_jobs=.65 if subset == 'training' else .35,
name=subset,
)
self.pools.append(pool)
features_ds = features_ds.unbatch()
# Pre-fetching batches can help with throughput
features_ds = features_ds.prefetch(per_job_batch_size)
# Combine the augmented audio samples with their corresponding labels
ds = tf.data.Dataset.zip((features_ds, labels_ds))
# Shuffle the data for each sample
# A perfect shuffle would use n_samples but this can slow down training,
# so we just shuffle batches of the data
ds = ds.shuffle(per_job_batch_size, reshuffle_each_iteration=True)
# At this point we have a flat dataset of x,y tuples
# Batch the data as necessary for training
ds = ds.batch(my_model.batch_size)
# Pre-fetch a couple training batches to aid throughput
ds = ds.prefetch(2)
return ds
my_model.dataset = MyDataset()
#################################################
# Audio Classifier Settings
#
# These are additional parameters to include in
# the generated .tflite model file.
# The settings are used by the ble_audio_classifier app
# NOTE: Corresponding command-line options will override these values.
# Controls the smoothing.
# Drop all inference results that are older than <now> minus window_duration
# Longer durations (in milliseconds) will give a higher confidence that the results are correct, but may miss some commands
my_model.model_parameters['average_window_duration_ms'] = 100
# Define a specific detection threshold for each class
#my_model.model_parameters['detection_threshold'] = 235
my_model.model_parameters['detection_threshold_list'] = list(map(lambda x: int(x*255), [.95, .95, .94, .94, .99, .99, 1.0]))
# Amount of milliseconds to wait after a keyword is detected before detecting the SAME keyword again
# A different keyword may be detected immediately after
my_model.model_parameters['suppression_ms'] = 1000
# The minimum number of inference results to average when calculating the detection value
my_model.model_parameters['minimum_count'] = 1
# Set the volume gain scaler (i.e. amplitude) to apply to the microphone data. If 0 or omitted, no scaler is applied
my_model.model_parameters['volume_gain'] = 0.0
# This the amount of time in milliseconds between audio processing loops
# Since we're using the audio detection block, we want this to be as short as possible
my_model.model_parameters['latency_ms'] = 10
# Enable verbose inference results
my_model.model_parameters['verbose_model_output_logs'] = False
#################################################
# Student/Teacher training config
#
def get_teacher_h5_path(try_archive=False, check_exists=True) -> str:
"""Return the file path to the trained "teacher" keras model"""
ext = '.teacher.test.h5' if my_model.test_mode_enabled else '.teacher.h5'
retval = None
if try_archive:
try:
retval = my_model.get_archive_file(f'{my_model.name}{ext}')
except:
pass
if retval is None:
retval = my_model.model_specification_path.replace('.py', ext)
if check_exists and not os.path.exists(retval):
raise RuntimeError(
f'Teacher keras model not found: {retval}\n'
'Have you trained the teacher model first?\n'
'e.g.:\nexport TRAIN_TEACHER=1\n'
'mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2'
)
return retval
def prepare_teacher_or_student_model(train_teacher:bool=None):
"""This prepares the model for "teacher" or "student" training
This is based on the given train_teacher argument or enviroment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER
"""
# Use the given argument or retrieve the TRAIN_TEACHER environment variable
if train_teacher is None:
train_teacher = os.environ.get('TRAIN_TEACHER', '0') == '1'
my_model.ssh_environment = dict(
TRAIN_TEACHER='1' if train_teacher else '0'
)
# If we're training the teacher then update the model properties for that
if train_teacher:
my_model.tflite_converter = None
my_model.build_model_function = my_teacher_model_builder
my_model.on_save_keras_model = my_teacher_model_saver
my_model.early_stopping = dict(
monitor='val_accuracy',
mode='auto',
verbose=1,
patience=25,
min_delta=0.0001
)
teacher_h5_path = get_teacher_h5_path(check_exists=False)
my_model.ssh_upload_files = [os.path.basename(teacher_h5_path)]
# Download the teacher's keras model (.h5) as keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5 after training completes
my_model.ssh_download_files = [f'~/.mltk/models/{my_model.name}/{os.path.basename(my_model.h5_log_dir_path)}|{os.path.basename(teacher_h5_path)}']
else:
# Otherwise we're training the student model
my_model.build_model_function = my_student_model_builder
my_model.on_save_keras_model = my_student_model_saver
my_model.tflite_converter['optimizations'] = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
my_model.tflite_converter['supported_ops'] = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_input_type'] = np.int8
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_output_type'] = np.int8
# Automatically generate a representative dataset from the validation data
my_model.tflite_converter['representative_dataset'] = 'generate'
# Upload the teacher's keras model (.h5) as keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.teacher.h5 before training starts
my_model.ssh_upload_files = [os.path.basename(get_teacher_h5_path())]
# By default, when this model is loaded,
# Prepare the teacher or student model based on the environment variable: TRAIN_TEACHER
prepare_teacher_or_student_model()
##########################################################################################
# The following allows for running this model training script directly, e.g.:
# python keyword_spotting_pacman_v2.py
#
# Note that this has the same functionality as:
# mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2
#
if __name__ == '__main__':
from mltk import cli
# Setup the CLI logger
cli.get_logger(verbose=True)
# If this is true then this will do a "dry run" of the model testing
# If this is false, then the model will be fully trained
test_mode_enabled = True
# Train the "teacher" model
# This does the same as issuing the command: export TRAIN_TEACHER=1 && mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2-test --clean
prepare_teacher_or_student_model(train_teacher=True)
train_results = mltk_core.train_model(my_model, clean=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(train_results)
# Train the "student" model
# This does the same as issuing the command: export TRAIN_TEACHER=0 && mltk train keyword_spotting_pacman_v2-test --clean
prepare_teacher_or_student_model(train_teacher=False)
train_results = mltk_core.train_model(my_model, clean=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(train_results)
# Evaluate the model against the quantized .h5 (i.e. float32) model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk evaluate keyword_spotting_pacman_v2-test
tflite_eval_results = mltk_core.evaluate_model(my_model, verbose=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(tflite_eval_results)
# Profile the model in the simulator
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk profile keyword_spotting_pacman_v2-test
profiling_results = mltk_core.profile_model(my_model, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(profiling_results)