siamese_contrastive¶
Source code: siamese_contrastive.py
This example was adapted from https://keras.io/examples/vision/siamese_contrastive.
Siamese Networks are neural networks which share weights between two or more sister networks, each producing embedding vectors of its respective inputs.
In supervised similarity learning, the networks are then trained to maximize the contrast (distance) between embeddings of inputs of different classes, while minimizing the distance between embeddings of similar classes, resulting in embedding spaces that reflect the class segmentation of the training inputs.
Commands¶
# Do a "dry run" test training of the model
mltk train siamese_contrastive-test
# Train the model
mltk train siamese_contrastive
# Evaluate the trained model .tflite model
mltk evaluate siamese_contrastive --tflite
# Profile the model in the MVP hardware accelerator simulator
mltk profile siamese_contrastive --accelerator MVP
# Profile the model on a physical development board
mltk profile siamese_contrastive --accelerator MVP --device
# Directly invoke the model script
python siamese_contrastive.py
Model Summary¶
> mltk summarize siamese_contrastive --tflite --build
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | Input(s) | Output(s) | Config |
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | quantize | 28x28x1 (float32) | 28x28x1 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 1 | quantize | 28x28x1 (float32) | 28x28x1 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 2 | conv_2d | 28x28x1 (int8) | 24x24x4 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:none |
| | | 5x5x1 (int8) | | |
| | | 4 (int32) | | |
| 3 | tanh | 24x24x4 (int8) | 24x24x4 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 4 | average_pool_2d | 24x24x4 (int8) | 12x12x4 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 5 | conv_2d | 12x12x4 (int8) | 8x8x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:none |
| | | 5x5x4 (int8) | | |
| | | 16 (int32) | | |
| 6 | tanh | 8x8x16 (int8) | 8x8x16 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 7 | average_pool_2d | 8x8x16 (int8) | 4x4x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 8 | reshape | 4x4x16 (int8) | 256 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| | | 2 (int32) | | |
| 9 | conv_2d | 28x28x1 (int8) | 24x24x4 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:none |
| | | 5x5x1 (int8) | | |
| | | 4 (int32) | | |
| 10 | tanh | 24x24x4 (int8) | 24x24x4 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 11 | average_pool_2d | 24x24x4 (int8) | 12x12x4 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 12 | conv_2d | 12x12x4 (int8) | 8x8x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:none |
| | | 5x5x4 (int8) | | |
| | | 16 (int32) | | |
| 13 | tanh | 8x8x16 (int8) | 8x8x16 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 14 | average_pool_2d | 8x8x16 (int8) | 4x4x16 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 15 | reshape | 4x4x16 (int8) | 256 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| | | 2 (int32) | | |
| 16 | fully_connected | 256 (int8) | 10 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 256 (int8) | | |
| | | 10 (int32) | | |
| 17 | tanh | 10 (int8) | 10 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 18 | quantize | 10 (int8) | 10 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 19 | fully_connected | 256 (int8) | 10 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 256 (int8) | | |
| | | 10 (int32) | | |
| 20 | tanh | 10 (int8) | 10 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 21 | quantize | 10 (int8) | 10 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 22 | concatenation | 10 (int8) | 20 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=10 |
| | | 10 (int8) | | |
| 23 | fully_connected | 20 (int8) | 64 (int8) | Activation:relu |
| | | 20 (int8) | | |
| | | 64 (int32) | | |
| 24 | fully_connected | 64 (int8) | 16 (int8) | Activation:relu |
| | | 64 (int8) | | |
| | | 16 (int32) | | |
| 25 | fully_connected | 16 (int8) | 1 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 16 (int8) | | |
| | | 1 (int32) | | |
| 26 | logistic | 1 (int8) | 1 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| 27 | dequantize | 1 (int8) | 1 (float32) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
+-------+-----------------+-------------------+----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Total MACs: 327.440 k
Total OPs: 676.823 k
Name: siamese_contrastive
Version: 1
Description: Image similarity estimation using a Siamese Network with a contrastive loss
classes: []
hash: 400f59a4a68872982f23f08a9de3fe92
date: 2022-02-04T18:55:43.645Z
runtime_memory_size: 11368
.tflite file size: 17.4kB
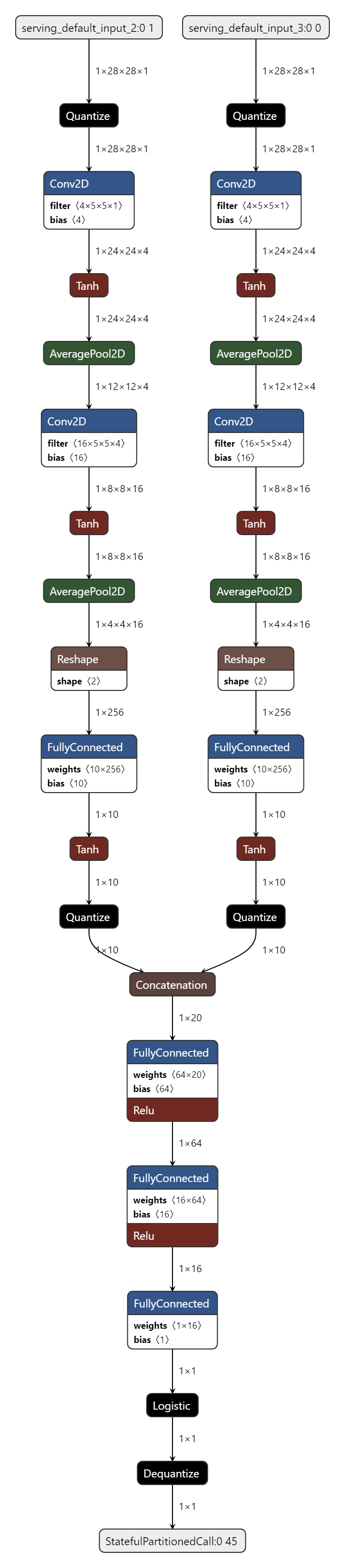
Model Diagram¶
mltk view siamese_contrastive --tflite --build
Model Specification¶
from typing import Union
import random
import logging
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import numpy as np
import mltk.core as mltk_core
from mltk.core import (
load_tflite_or_keras_model,
KerasModel,
TfliteModel,
EvaluationResults
)
from mltk.core.tflite_model.tflite_model import TfliteModel
from mltk.datasets.image import mnist
# Instantiate the MltkModel object with the following 'mixins':
# - TrainMixin - Provides classifier model training operations and settings
# - DatasetMixin - Generic data generation operations and settings
# @mltk_model # NOTE: This tag is required for this model be discoverable
class MyModel(
mltk_core.MltkModel,
mltk_core.TrainMixin,
mltk_core.DatasetMixin,
mltk_core.EvaluateMixin
):
def load_dataset(
self,
subset: str,
test:bool = False,
**kwargs
):
super().load_dataset(subset)
(x_train_val, y_train_val), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# Change the data type to a floating point format
x_train_val = x_train_val.astype("float32")
x_test = x_test.astype("float32")
# Keep 50% of train_val in validation set
x_train, x_val = x_train_val[:30000], x_train_val[30000:]
y_train, y_val = y_train_val[:30000], y_train_val[30000:]
del x_train_val, y_train_val
# If we're testing, then just use a small subset
if test:
l = self.batch_size*3
x_train, y_train = x_train[:l], y_train[:l]
x_val, y_val = x_val[:l], y_val[:l]
#x_test, y_test = x_test[:32], y_test[:32]
# make train pairs
pairs_train, labels_train = make_pairs(x_train, y_train)
# pairs_train.shape = (60000, 2, 28, 28)
# We have 60,000 pairs
# Each pair contains 2 images
# Each image has shape (28, 28)
x_train_1 = pairs_train[:, 0] # x_train_1.shape is (60000, 28, 28)
x_train_2 = pairs_train[:, 1]
# make validation pairs
pairs_val, labels_val = make_pairs(x_val, y_val)
x_val_1 = pairs_val[:, 0] # x_val_1.shape = (60000, 28, 28)
x_val_2 = pairs_val[:, 1]
# make test pairs
pairs_test, labels_test = make_pairs(x_test, y_test)
x_test_1 = pairs_test[:, 0] # x_test_1.shape = (20000, 28, 28)
x_test_2 = pairs_test[:, 1]
if subset == 'evaluation':
self.x = [x_test_1, x_test_2]
self.y = labels_test
else:
self.x = [x_train_1, x_train_2]
self.y = labels_train
self.validation_data = ([x_val_1, x_val_2], labels_val)
def make_pairs(x, y):
"""Creates a tuple containing image pairs with corresponding label.
Arguments:
x: List containing images, each index in this list corresponds to one image.
y: List containing labels, each label with datatype of `int`.
Returns:
Tuple containing two numpy arrays as (pairs_of_samples, labels),
where pairs_of_samples' shape is (2len(x), 2,n_features_dims) and
labels are a binary array of shape (2len(x)).
"""
num_classes = max(y) + 1
digit_indices = [np.where(y == i)[0] for i in range(num_classes)]
pairs = []
labels = []
for idx1 in range(len(x)):
# add a matching example
x1 = x[idx1]
label1 = y[idx1]
idx2 = random.choice(digit_indices[label1])
x2 = x[idx2]
pairs += [[x1, x2]]
labels += [1]
# add a non-matching example
label2 = random.randint(0, num_classes - 1)
while label2 == label1:
label2 = random.randint(0, num_classes - 1)
idx2 = random.choice(digit_indices[label2])
x2 = x[idx2]
pairs += [[x1, x2]]
labels += [0]
return np.array(pairs), np.array(labels).astype("float32")
class ContrastiveLoss(keras.losses.Loss):
def __init__(
self,
margin=1,
**kwargs
):
"""Calculates the contrastive loss.
Contrastive loss = mean( (1-true_value) * square(prediction) +
true_value * square( max(margin-prediction, 0) ))
Arguments:
margin: Integer, defines the baseline for distance for which pairs
should be classified as dissimilar. - (default is 1).
Returns:
A tensor containing contrastive loss as floating point value.
"""
super(ContrastiveLoss, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.margin = margin
def call(self, y_true, y_pred):
"""
Arguments:
y_true: List of labels, each label is of type float32.
y_pred: List of predictions of same length as of y_true,
each label is of type float32.
"""
square_pred = tf.math.square(y_pred)
margin_square = tf.math.square(tf.math.maximum(self.margin - (y_pred), 0))
return tf.math.reduce_mean(
(1 - y_true) * square_pred + (y_true) * margin_square
)
def get_config(self):
"""Returns the config dictionary for a `Loss` instance."""
return {'reduction': self.reduction, 'name': self.name, 'margin': self.margin}
# Provided two tensors t1 and t2
# Euclidean distance = sqrt(sum(square(t1-t2)))
def euclidean_distance(vects):
"""Find the Euclidean distance between two vectors.
Arguments:
vects: List containing two tensors of same length.
Returns:
Tensor containing euclidean distance
(as floating point value) between vectors.
"""
x = vects[0]
y = vects[1]
sum_square = tf.math.reduce_sum(tf.math.square(x - y), axis=1, keepdims=True)
return tf.math.sqrt(tf.math.maximum(sum_square, tf.keras.backend.epsilon()))
def my_model_builder(my_model: MyModel):
input = layers.Input(my_model.input_shape)
x = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(input)
x = layers.Conv2D(4, (5, 5), activation="tanh")(x)
x = layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(16, (5, 5), activation="tanh")(x)
x = layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
x = layers.Flatten()(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = layers.Dense(10, activation="tanh")(x)
embedding_network = keras.Model(input, x)
input_1 = layers.Input(my_model.input_shape)
input_2 = layers.Input(my_model.input_shape)
# As mentioned above, Siamese Network share weights between
# tower networks (sister networks). To allow this, we will use
# same embedding network for both tower networks.
tower_1 = embedding_network(input_1)
tower_2 = embedding_network(input_2)
# Technically, we should be calculating the euclidean distance
# as a model layer.
# However, TFLM doesn't not support the SQUARED_DIFFERENCE kernel
# So, as a work-around, we just use a dense layer to emulate it
#merge_layer = layers.Lambda(euclidean_distance)([tower_1, tower_2])
#normal_layer = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(merge_layer)
conc = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()([tower_1, tower_2])
dense_1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation="relu")(conc)
normal_layer = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation="relu")(dense_1)
output_layer = layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(normal_layer)
keras_model = keras.Model(inputs=[input_1, input_2], outputs=output_layer)
keras_model.compile(
loss=my_model.loss,
optimizer=my_model.optimizer,
metrics=my_model.metrics
)
return keras_model
def my_model_evaluator(
my_model:MyModel,
built_model:Union[KerasModel, TfliteModel],
eval_dir:str,
logger:logging.Logger,
**kwargs
) -> EvaluationResults:
results = EvaluationResults(name=my_model.name)
if isinstance(built_model, KerasModel):
eval_loss, eval_accuracy = built_model.evaluate(
x=my_model.x,
y=my_model.y,
batch_size=my_model.batch_size,
verbose=1
)
results['overall_accuracy'] = eval_accuracy
else:
x1, x2 = my_model.x
y = my_model.y
batch_size = min(my_model.batch_size, len(y))
if my_model.test_mode_enabled:
x1 = x1[:3]
x2 = x2[:3]
y = y[:3]
batch_size = 3
tflite_interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path=built_model.path)
input_tensors = tflite_interpreter.get_input_details()
output_tensor = tflite_interpreter.get_output_details()[0]
new_input_shape = (batch_size,) + my_model.input_shape
new_output_shape = (batch_size,) + tuple(output_tensor['shape'][1:])
for input_tensor in input_tensors:
tflite_interpreter.resize_tensor_input(input_tensor['index'], new_input_shape)
tflite_interpreter.resize_tensor_input(output_tensor['index'], new_output_shape)
tflite_interpreter.allocate_tensors()
n_samples = 0
n_correct = 0
offset = 0
while offset + batch_size <= len(y):
x1_batch = np.expand_dims(x1[offset:offset+batch_size], axis=-1)
x2_batch = np.expand_dims(x2[offset:offset+batch_size], axis=-1)
tflite_interpreter.set_tensor(input_tensors[0]['index'], x1_batch)
tflite_interpreter.set_tensor(input_tensors[1]['index'], x2_batch)
tflite_interpreter.invoke()
y_pred = tflite_interpreter.get_tensor(output_tensor['index'])
n_samples += len(y_pred)
for i, pred in enumerate(y_pred):
# If the prediction is within 20% of the actual
# then we consider it correct
if abs(pred - y[offset + i]) < .2:
n_correct += 1
y_pred = None
offset += batch_size
results['overall_accuracy'] = n_correct / n_samples
return results
my_model = MyModel()
my_model.version = 1
my_model.description = 'Image similarity estimation using a Siamese Network with a contrastive loss'
my_model.epochs = 10
my_model.batch_size = 16
my_model.loss = ContrastiveLoss(margin=1.0)
my_model.metrics = ['accuracy']
my_model.optimizer = 'RMSprop'
my_model.build_model_function = my_model_builder
my_model.input_shape = (28, 28, 1)
my_model.eval_custom_function = my_model_evaluator
# We need to save reference to the custom loss function
# so that we can load the .h5 file
# See https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras/save_and_serialize#registering_the_custom_object
my_model.keras_custom_objects['ContrastiveLoss'] = ContrastiveLoss
#################################################
# TF-Lite converter settings
my_model.tflite_converter['optimizations'] = ['DEFAULT']
my_model.tflite_converter['supported_ops'] = ['TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8']
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_input_type'] = 'float32'
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_output_type'] = 'float32'
# generate a representative dataset from the validation data
my_model.tflite_converter['representative_dataset'] = 'generate'
# generate a representative dataset from the validation data
def my_representative_dataset_generator():
batch_size = my_model.batch_size
x_1, x_2 = my_model.x
retval = []
offset = 0
for index in range(len(x_1) // batch_size):
if index >= 100:
break
x1 = np.expand_dims(x_1[offset:offset+batch_size], axis=-1)
x2 = np.expand_dims(x_2[offset:offset+batch_size], axis=-1)
retval.append([x1, x2])
offset += batch_size
return retval
my_model.tflite_converter['representative_dataset'] = my_representative_dataset_generator
#################################################
# Custom Commands
def visualize(x, labels, to_show=6, num_col=3, predictions=None, test=False):
"""Creates a plot of pairs and labels, and prediction if it's test dataset.
Arguments:
pairs: List if input samples,
[(Number of pairs, 28, 28), (Number of pairs, 28, 28)]
to_show: Int, number of examples to visualize (default is 6)
`to_show` must be an integral multiple of `num_col`.
Otherwise it will be trimmed if it is greater than num_col,
and incremented if if it is less then num_col.
num_col: Int, number of images in one row - (default is 3)
For test and train respectively, it should not exceed 3 and 7.
predictions: Numpy Array of predictions with shape (to_show, 1) -
(default is None)
Must be passed when test=True.
test: Boolean telling whether the dataset being visualized is
train dataset or test dataset - (default False).
Returns:
None.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define num_row
# If to_show % num_col != 0
# trim to_show,
# to trim to_show limit num_row to the point where
# to_show % num_col == 0
#
# If to_show//num_col == 0
# then it means num_col is greater then to_show
# increment to_show
# to increment to_show set num_row to 1
num_row = to_show // num_col if to_show // num_col != 0 else 1
# `to_show` must be an integral multiple of `num_col`
# we found num_row and we have num_col
# to increment or decrement to_show
# to make it integral multiple of `num_col`
# simply set it equal to num_row * num_col
to_show = num_row * num_col
# Plot the images
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_row, num_col, figsize=(8, 2))
for i in range(to_show):
# If the number of rows is 1, the axes array is one-dimensional
if num_row == 1:
ax = axes[i % num_col]
else:
ax = axes[i // num_col, i % num_col]
ax.imshow(tf.concat([x[0][i], x[1][i]], axis=1), cmap="gray")
ax.set_axis_off()
if test:
ax.set_title("True: {} | Pred: {:.5f}".format(labels[i], predictions[i][0]))
else:
ax.set_title("Label: {}".format(labels[i]))
# if test:
# plt.tight_layout(rect=(0, 0, 1.9, 1.9), w_pad=0.0)
# else:
# plt.tight_layout(rect=(0, 0, 1.5, 1.5))
plt.show()
# Register the "visualize" custom command
import typer
@my_model.cli.command('visualize')
def visualize_custom_command(
predict:bool = typer.Option(False, '--predict',
help='Include the trained model predictions in the displayed results'
),
count:int = typer.Option(4, '--count',
help='Number of samples to display'
),
col:int = typer.Option(3, '--col',
help='Number of sample per column'
)
):
"""Custom command to view training dataset
\b
Invoke this command with:
mltk custom siamese_contrastive visualize
mltk custom siamese_contrastive visualize --predict
"""
if predict:
my_model.load_dataset(subset='validation')
# Load the trained .h5 model
keras_model = load_tflite_or_keras_model(my_model, model_type='h5')
predictions = keras_model.predict(my_model.x)
visualize(my_model.x, my_model.y, to_show=count, num_col=col, predictions=predictions, test=True)
else:
my_model.load_dataset(subset='training')
visualize(my_model.x, my_model.y, to_show=count, num_col=col)
my_model.unload_dataset()
##########################################################################################
# The following allows for running this model training script directly, e.g.:
# python siamese_contrastive.py
#
# Note that this has the same functionality as:
# mltk train siamese_contrastive
#
if __name__ == '__main__':
from mltk import cli
# Setup the CLI logger
cli.get_logger(verbose=False)
# If this is true then this will do a "dry run" of the model testing
# If this is false, then the model will be fully trained
test_mode_enabled = True
# Train the model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk train siamese_contrastive-test --clean
train_results = mltk_core.train_model(my_model, clean=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(train_results)
# Evaluate the model against the quantized .h5 (i.e. float32) model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk evaluate siamese_contrastive-test
tflite_eval_results = mltk_core.evaluate_model(my_model, verbose=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(tflite_eval_results)
# Profile the model in the simulator
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk profile siamese_contrastive-test
profiling_results = mltk_core.profile_model(my_model, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(profiling_results)