binary_classification¶
Binary classification (ResNetv1-10 with CIFAR10)
Source code: binary_classification.py
This demonstrates how to classify two images:
Cat
Dog
Using the CIFAR10 dataset.
The key points required for binary image classification are:
binary_crossentropyloss functionbinary“class mode” for the data generator, this makes it so the generated “y” vector is a 1D vectorOne dense unit in the final layer to do the actual classification
sigmoidactivation in the last layer of the model so that the output of the model is between 0 and 1
Commands¶
# Dump some of samples generated by this model
# using a custom command defined at this bottom
# of this model specification file
mltk custom binary_classification datagen_dump
# Do a "dry run" test training of the model
mltk train binary_classification-test
# Train the model
mltk train binary_classification
# Evaluate the trained model .tflite model
mltk evaluate binary_classification --tflite
# Profile the model in the MVP hardware accelerator simulator
mltk profile binary_classification --accelerator MVP
# Profile the model on a physical development board
mltk profile binary_classification --accelerator MVP --device
# Directly invoke the model script
python binary_classification.py
Model Summary¶
mltk summarize binary_classification --tflite
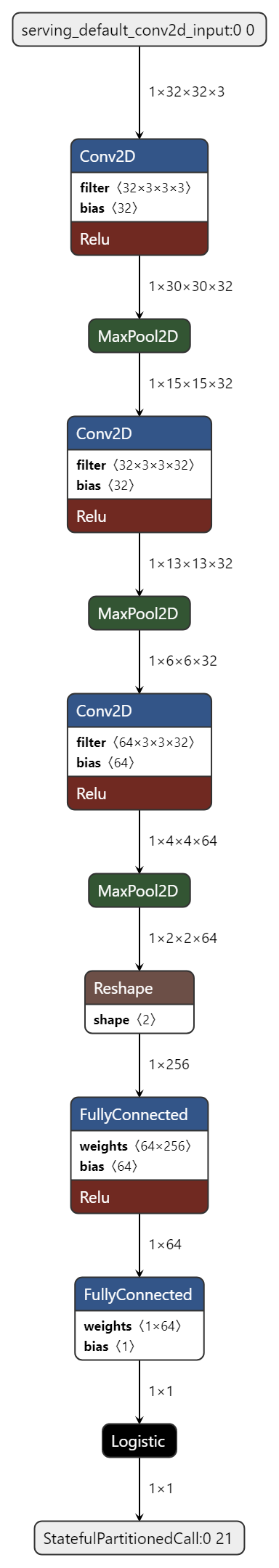
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Index | OpCode | Input(s) | Output(s) | Config |
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | conv_2d | 32x32x3 (int8) | 30x30x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x3 (int8) | | |
| | | 32 (int32) | | |
| 1 | max_pool_2d | 30x30x32 (int8) | 15x15x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 2 | conv_2d | 15x15x32 (int8) | 13x13x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x32 (int8) | | |
| | | 32 (int32) | | |
| 3 | max_pool_2d | 13x13x32 (int8) | 6x6x32 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 4 | conv_2d | 6x6x32 (int8) | 4x4x64 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:1x1 activation:relu |
| | | 3x3x32 (int8) | | |
| | | 64 (int32) | | |
| 5 | max_pool_2d | 4x4x64 (int8) | 2x2x64 (int8) | Padding:valid stride:2x2 filter:2x2 activation:none |
| 6 | reshape | 2x2x64 (int8) | 256 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
| | | 2 (int32) | | |
| 7 | fully_connected | 256 (int8) | 64 (int8) | Activation:relu |
| | | 256 (int8) | | |
| | | 64 (int32) | | |
| 8 | fully_connected | 64 (int8) | 1 (int8) | Activation:none |
| | | 64 (int8) | | |
| | | 1 (int32) | | |
| 9 | logistic | 1 (int8) | 1 (int8) | BuiltinOptionsType=0 |
+-------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Total MACs: 2.646 M
Total OPs: 5.363 M
Name: binary_classification
Version: 1
Description: Example: Binary classification - ResNetv1-10 with CIFAR10
Classes: cat, dog
hash: de33dd53e0afb91a365fd2fff0e4c461
date: 2022-02-11T17:32:37.986Z
runtime_memory_size: 38740
samplewise_norm.rescale: 0.0
samplewise_norm.mean_and_std: False
.tflite file size: 53.8kB
Model Diagram¶
mltk view binary_classification --tflite
Model Specification¶
import functools
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from mltk.core.preprocess.image.parallel_generator import ParallelImageDataGenerator
from mltk.datasets.image import cifar10
import mltk.core as mltk_core
# Instantiate the MltkModel object with the following 'mixins':
# - TrainMixin - Provides classifier model training operations and settings
# - ImageDatasetMixin - Provides image data generation operations and settings
# - EvaluateClassifierMixin - Provides classifier evaluation operations and settings
# @mltk_model # NOTE: This tag is required for this model be discoverable
class MyModel(
mltk_core.MltkModel,
mltk_core.TrainMixin,
mltk_core.ImageDatasetMixin,
mltk_core.EvaluateClassifierMixin
):
pass
my_model = MyModel()
# General parameters
my_model.version = 1
my_model.description = 'Example: Binary classification - ResNetv1-10 with CIFAR10'
#################################################
# Training parameters
my_model.epochs = 200
my_model.batch_size = 40
my_model.optimizer = 'adam'
my_model.metrics = ['accuracy']
my_model.loss = 'binary_crossentropy'
#################################################
# TF-Lite converter settings
my_model.tflite_converter['optimizations'] = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
my_model.tflite_converter['supported_ops'] = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_input_type'] = tf.int8 # can also be tf.float32
my_model.tflite_converter['inference_output_type'] = tf.int8
# generate a representative dataset from the validation data
my_model.tflite_converter['representative_dataset'] = 'generate'
#################################################
# Image Dataset Settings
# Default size for CIFAR10 dataset
input_height = 32
input_width = 32
input_depth = 3
# The classification type
my_model.class_mode = 'binary'
# The class labels found in your training dataset directory
my_model.classes = ['cat', 'dog']
# The input shape to the model. The dataset samples will be resized if necessary
my_model.input_shape = [input_height, input_width, input_depth]
def my_dataset_loader(model:MyModel):
(cifar10_x_train, cifar10_y_train), (cifar10_x_test, cifar10_y_test) = cifar10.load_data()
# Extract just the cat and dog samples
cats_and_dogs_x_train = []
cats_and_dogs_y_train = []
cats_and_dogs_x_test = []
cats_and_dogs_y_test = []
n_cat = 0
n_dog = 0
for x, y in zip(cifar10_x_train, cifar10_y_train):
if y == 3: # cat label, see https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html
if model.test_mode_enabled and n_cat > 100:
continue
cats_and_dogs_x_train.append(x)
cats_and_dogs_y_train.append(0) # cat maps to id 0, see the my_model.classes above
n_cat += 1
elif y == 5: # dog label
if model.test_mode_enabled and n_dog > 100:
continue
cats_and_dogs_x_train.append(x)
cats_and_dogs_y_train.append(1)
n_dog += 1
n_cat = 0
n_dog = 0
for x, y in zip(cifar10_x_test, cifar10_y_test):
if y == 3: # cat label, see https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html
if model.test_mode_enabled and n_cat > 100:
continue
cats_and_dogs_x_test.append(x)
cats_and_dogs_y_test.append(0) # cat maps to id 0, see the my_model.classes above
n_cat += 1
elif y == 5: # dog label
if model.test_mode_enabled and n_dog > 100:
continue
cats_and_dogs_x_test.append(x)
cats_and_dogs_y_test.append(1)
n_dog += 1
x_train = np.asarray(cats_and_dogs_x_train)
y_train = np.asarray(cats_and_dogs_y_train)
x_test = np.asarray(cats_and_dogs_x_test)
y_test = np.asarray(cats_and_dogs_y_test)
# Convert for training
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
# Scale to INT8 range (simple non-adaptive)
x_train = (x_train-128)/128
x_test = (x_test-128)/128
return x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test
my_model.dataset = functools.partial(my_dataset_loader, my_model)
##############################################################
# Training callbacks
#
my_model.datagen = ParallelImageDataGenerator(
cores=.35,
max_batches_pending=32,
rotation_range=15,
width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1,
horizontal_flip=True,
vertical_flip=True,
validation_augmentation_enabled=False
)
##############################################################
# Model Layout
def my_model_builder(model: MyModel):
keras_model = Sequential()
keras_model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), input_shape=model.input_shape))
keras_model.add(layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
keras_model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3)))
keras_model.add(layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
keras_model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3)))
keras_model.add(layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
keras_model.add(layers.Flatten()) # this converts our 3D feature maps to 1D feature vectors
keras_model.add(layers.Dense(64))
keras_model.add(layers.Activation('relu'))
keras_model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
keras_model.add(layers.Dense(1)) # Binary so we only need 1 unit for this layer
keras_model.add(layers.Activation('sigmoid')) # Binary so we want the activation to be between 0 and 1 which is what the sigmoid function produces
keras_model.compile(
loss=model.loss,
optimizer=model.optimizer,
metrics=model.metrics
)
return keras_model
my_model.build_model_function = my_model_builder
# Register the "datagen_dump" custom command
import typer
@my_model.cli.command('datagen_dump')
def datagen_dump_custom_command(
count:int = typer.Option(100, '--count',
help='Number of samples to dump'
),
):
"""Custom command to dump the augmented samples
\b
Invoke this command with:
mltk custom binary_classification datagen_dump --count 20
"""
my_model.datagen.save_to_dir = my_model.create_log_dir('datagen_dump', delete_existing=True)
my_model.datagen.debug = True
my_model.datagen.cores = 1
my_model.datagen.max_batches_pending = 1
my_model.datagen.batch_size = 1
my_model.load_dataset(subset='training')
for i, _ in enumerate(my_model.x):
if i >= count:
break
my_model.unload_dataset()
print(f'Generated data dump to: {my_model.datagen.save_to_dir}')
##########################################################################################
# The following allows for running this model training script directly, e.g.:
# python binary_classification.py
#
# Note that this has the same functionality as:
# mltk train binary_classification
#
if __name__ == '__main__':
from mltk import cli
# Setup the CLI logger
cli.get_logger(verbose=False)
# If this is true then this will do a "dry run" of the model testing
# If this is false, then the model will be fully trained
test_mode_enabled = True
# Train the model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk train binary_classification-test --clean
train_results = mltk_core.train_model(my_model, clean=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(train_results)
# Evaluate the model against the quantized .h5 (i.e. float32) model
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk evaluate binary_classification-test
tflite_eval_results = mltk_core.evaluate_model(my_model, verbose=True, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(tflite_eval_results)
# Profile the model in the simulator
# This does the same as issuing the command: mltk profile binary_classification-test
profiling_results = mltk_core.profile_model(my_model, test=test_mode_enabled)
print(profiling_results)