Unify Framework
Introduction
The Unify Framework provides software source code and binary packages for Raspberry Pi 4 to help build an IoT gateway product. The Unify Framework allows an IoT service to control and manage end nodes using supported wireless PHY radio protocol, which is Z-Wave protocol, provided by Silicon Labs. The Unify Framework uses the Unify Controller Language (UCL) as an internal abstraction layer to seamlessly control various end nodes that are enabled with multiple wireless PHY radios. The detailed architecture of the Unify Framework is described in the Unify Framework Specification.
The Unify Framework uses Unify Framework library to decouple API modules from the PHY drivers. This facilitates code reuse and enables easily adding new high-level APIs without the need to modify the PHY drivers. The library provides a number of components that simplify the task of writing a PHY driver also known as a Protocol Controller.
Systems Overview
A Unify gateway consists of a Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) broker and a number of MQTT clients. The Unify Framework uses the Mosquitto MQTT broker.
The following diagram shows the overview of System with Unify Applications and their groupings and relation with other Unify Applications or MQTT broker.
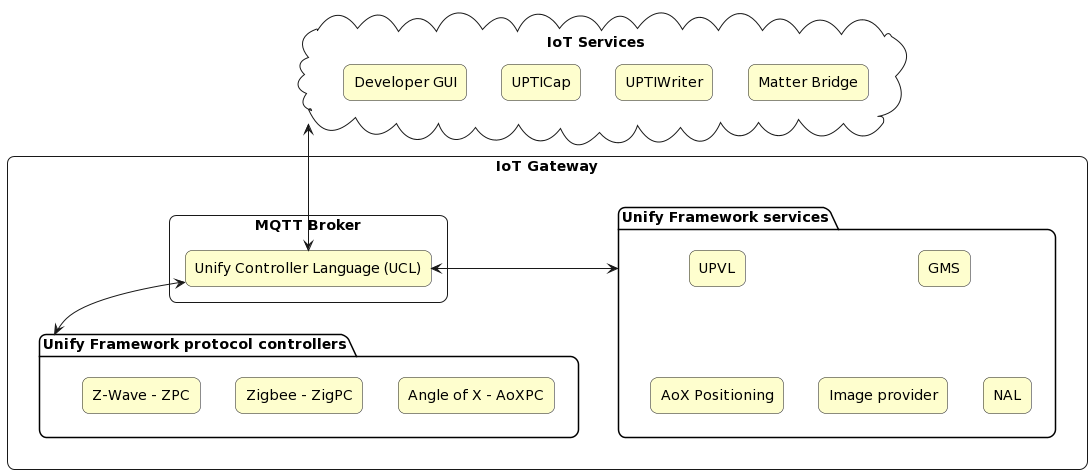
The Unify Framework was previously known as Unified IoT Controller or UIC for short. The old name can still be found in some parts of the Framework.
Unify Applications Overview
The Unify Framework contains the following applications:
The framework services work with the protocol controllers to facilitate different features such as group management, OTA updates etc. See links above for more details.
The IOT services interface with the MQTT broker to provide high level functionality on top of the Unify framework. See the link above for more information.
The Emulated End Device helps to emulate end device with user configured clusters or device emulating a specific device type. See the link above for more information.
Please read the Unify Framework User guide for details on configuring and running Unify Framework applications.
Overview of communication among Unify Framework Applications
All individual Unify applications communicate via MQTT. In this reference implementation, the Mosquitto MQTT broker is used which does not support clustering. As a result, all nodes connect to a single central broker.
MQTT implements a publisher-subscriber model, where all payloads are published to topics to which zero, one, or many clients can subscribe to. By default, publishers can publish to any topic and all subscribers can subscribe to any topic. MQTT has the notion of access-control but that functionality is currently not used by Unify.
A publisher does not get notified (by the broker) if a subscriber has received its message. All QoS functionality is handled by the broker.
MQTT has the notion of message-retention, i.e., a message can be retained on a topic and delivered to any future subscribers. Only a single message is retained on a given topic at a time. Publishing an MQTT-message with an empty (zero bytes) payload to a topic will clear its previously retained message.
In Unify, all message payloads are JSON-objects. Some of the Unify topics (e.g., commands) may not require any data, but they will require at least an empty JSON object (e.g., {}).
Unify Framework Release Notes
The Unify Framework release notes can be found on GitHub.
Unify Framework Developer Guides
The developer guides for the Unify Framework includes the Unify Developer Guide and the Unify Library Overview.