Verifies interrupt frequency is within bounds. More...
Classes | |
| struct | sl_iec60730_irq_execution_bounds_t |
| struct | sl_iec60730_irq_fail_t |
| struct | sl_iec60730_irq_cfg_t |
Macros | |
| #define | IEC60730_MAX_IRQ_CHECK 32 |
| #define | SL_IEC60730_IRQ_TYPE_VARIABLE uint8_t |
| Data type for iec60730_IRQExecCount variables. | |
| #define | SL_IEC60730_IRQ_STATUS_ENABLE 0 |
| Enable using sl_iec60730_get_irq_index_failed() function to get the value of failed irqs. | |
Functions | |
| void | sl_iec60730_irq_reset_fail_result (void) |
| sl_iec60730_irq_fail_t * | sl_iec60730_get_irq_index_failed (void) |
| void | sl_iec60730_irq_init (sl_iec60730_irq_cfg_t *irq_cfg_ptr) |
| void | sl_iec60730_irq_reset_counter (void) |
| void | sl_iec60730_irq_check (void) |
Detailed Description
Verifies interrupt frequency is within bounds.
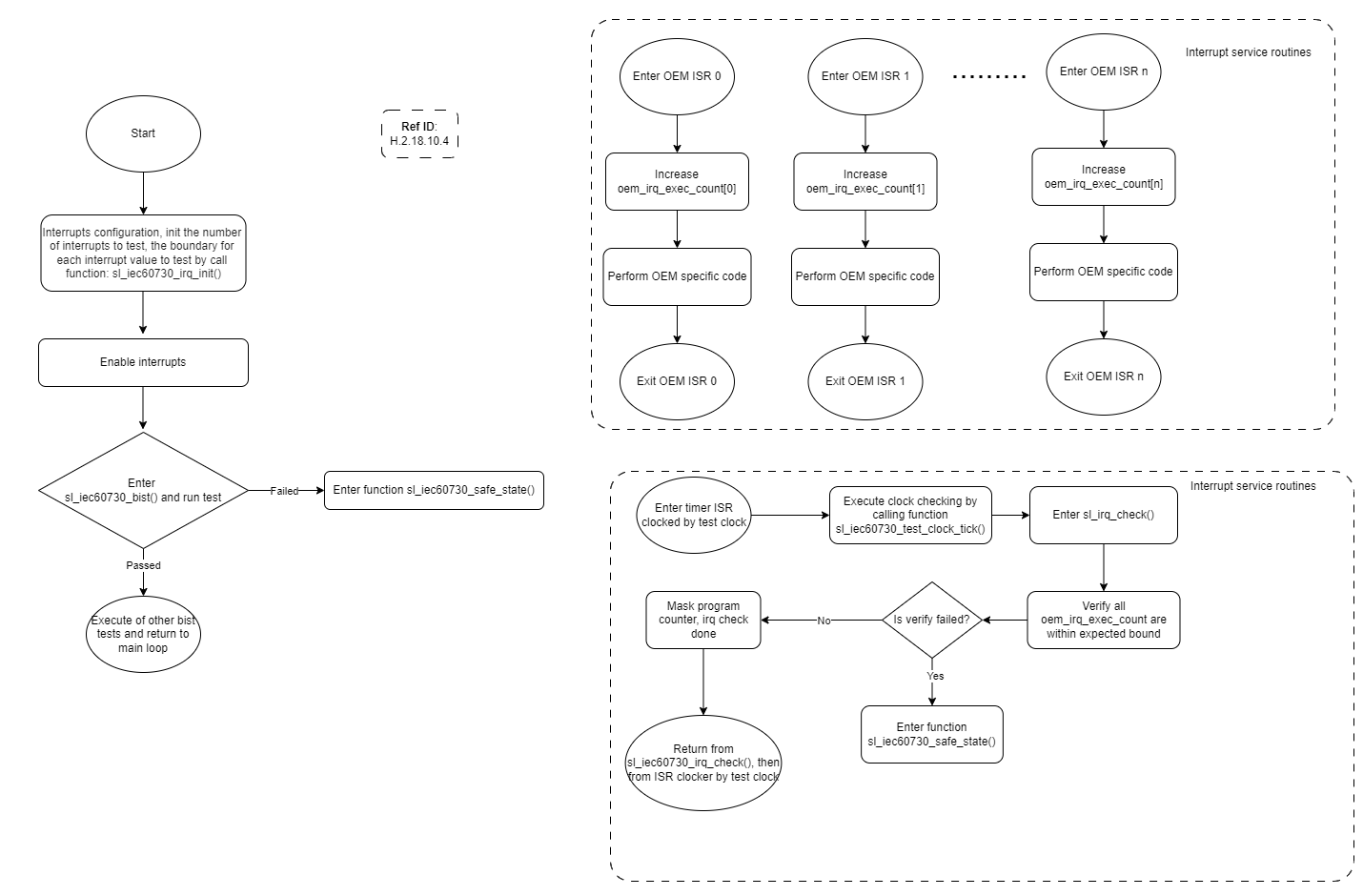
The interrupt plausibility test checks that enabled interrupts are executing at a frequency that is within expected minimum and maximum bounds every test timer period.
OEM firmware is responsible for setting expected minimum and maximum bounds for each enabled interrupt in the oem_irq_freq_bounds structure. The OEM is also responsible for incrementing the element in the oem_irq_exec_count array inside each enabled interrupt. In sl_iec60730_irq_check(), which executes as part of the test timer-driven tests of the BIST, this counter array is compared with the defined bounds to determine whether each interrupt is operating within safe parameters.
Hardware Architecture
Most hardware-implemented peripherals in Silicon Labs EFR32 devices offer the ability to vector to an interrupt service routine in order to quickly respond peripheral-related events and state updates.
In order to vector to an interrupt from executing foreground code, hardware pushes the program counter to the stack and vectors to a hardware-defined entry in a vector table stored in non-volatile memory in a region of Flash. The code of the interrupt service routine is either stored directly within this table entry, or stored elsewhere in memory and accessed through a jump instruction placed in the vector table, depending on the size of the interrupt service routine.
Once the function body of the interrupt service routine has completed executing, the program counter is pop from the stack and returns to foreground code to continue execution.
Each interrupt has a flag in a register that must be cleared inside the interrupt service routine function to signal that the interrupt has been processed in firmware. Failure to clear this flag inside the function body will result in the hardware immediately vectoring back to the interrupt.
Failure Risks
It is the OEM's responsibility to accurately estimate the frequency of each enabled interrupt in a firmware project. For interrupts that are asynchronous and may not execute at all within a test timer period, the lower bounds for the interrupt should be set to 0.
It is also the OEM's responsibility to increment values in oem_irq_exec_count once and only once per interrupt execution. Failure to include this incrementing command will result in an interrupt that appears to be executing below minimum defined bounds, which will force safe state entry.
The OEM should also be mindful of all hardware-related constraints of each interrupt. Failure to clear an interrupt flag inside an interrupt service routine will cause the routine to execute repeatedly, which will increment an oem_irq_exec_count entry beyond upper bounds and cause a safe state entry.
The OEM must also perform a bounds check on the element in oem_irq_exec_count being incremented to ensure that the counter does not exceed the upper bounds defined by its data type and overflow back to 0. Failure to perform this bounds check could have the effect of creating a passing IRQ plausibility test when the interrupt is actually running outside of defined limits.
Software Architecture
The interrupt plausibility test function relies on an array of counters called oem_irq_exec_count, stored in volatile memory and an array of struct sl_iec60730_irq_execution_bounds_t found in non-volatile memory and called oem_irq_freq_bounds. OEM firmware increments bytes in oem_irq_exec_count during execution of each enabled interrupt service routine. When the test timer interrupt occurs, sl_iec60730_irq_check() executes. Inside this function, firmware compares the count values to the bound values, and sets iec60730_safety_check by called function sl_iec60730_safety_check_error_occur to SL_IEC60730_INTERRUPT_FAIL if a count exceeds either the minimum or maximum bounds. The next execution of the BIST routine will detect the SL_IEC60730_TEST_FAILED state and enter safe state. A flowchart of this functionality is shown in Figure 1 .
For more information on configuration of the test timer, please see System Clock Check.
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ IEC60730_MAX_IRQ_CHECK
| #define IEC60730_MAX_IRQ_CHECK 32 |
The maximum number of interrupted users that can be used for testing. The param passed to the init function sl_iec60730_irq_init() must have a size value smaller than this value
Function Documentation
◆ sl_iec60730_get_irq_index_failed()
| sl_iec60730_irq_fail_t* sl_iec60730_get_irq_index_failed | ( | void | ) |
public IEC60730 Get The Location Of The Failed IRQ
- Returns
- pointer type sl_iec60730_irq_fail_t point to variable containing the errors that occurred and the number of errors
This function return a iec60730_irq_fail_result. That variable contains the number of failed irq checks and stores the failed interrupt value in bits.
◆ sl_iec60730_irq_check()
| void sl_iec60730_irq_check | ( | void | ) |
public IEC60730 Interrupt Plausibility Check
- Returns
- None.
This function compares each entry in oem_irq_exec_count with its corresponding bounds defined in oem_irq_freq_bounds. If the entry is found to exceed the defined bounds, iec60730_safety_check is set to SL_IEC60730_INTERRUPT_FAIL. Otherwise no action is taken. The function ends by setting IEC60730_INTERRUPT_COMPLETE.
◆ sl_iec60730_irq_init()
| void sl_iec60730_irq_init | ( | sl_iec60730_irq_cfg_t * | irq_cfg_ptr | ) |
public IEC60730 Interrupt Init
- Parameters
-
irq_cfg_ptr input pointer point to value config by user
- Returns
- None.
This function set a pointer point to address oem_irq_freq_bounds min and max and oem_irq_exec_count. To initialize test values for the sl_iec60730_irq_check() function.
◆ sl_iec60730_irq_reset_counter()
| void sl_iec60730_irq_reset_counter | ( | void | ) |
public IEC60730 Interrupt Reset Counter
- Returns
- None.
This function reset counter oem_irq_exec_count to 0
◆ sl_iec60730_irq_reset_fail_result()
| void sl_iec60730_irq_reset_fail_result | ( | void | ) |
public IEC60730 Reset IRQ Failed Results
- Returns
- None.
This function reset local counter irq fail iec60730_irq_fail_result to 0
 1.8.17
1.8.17